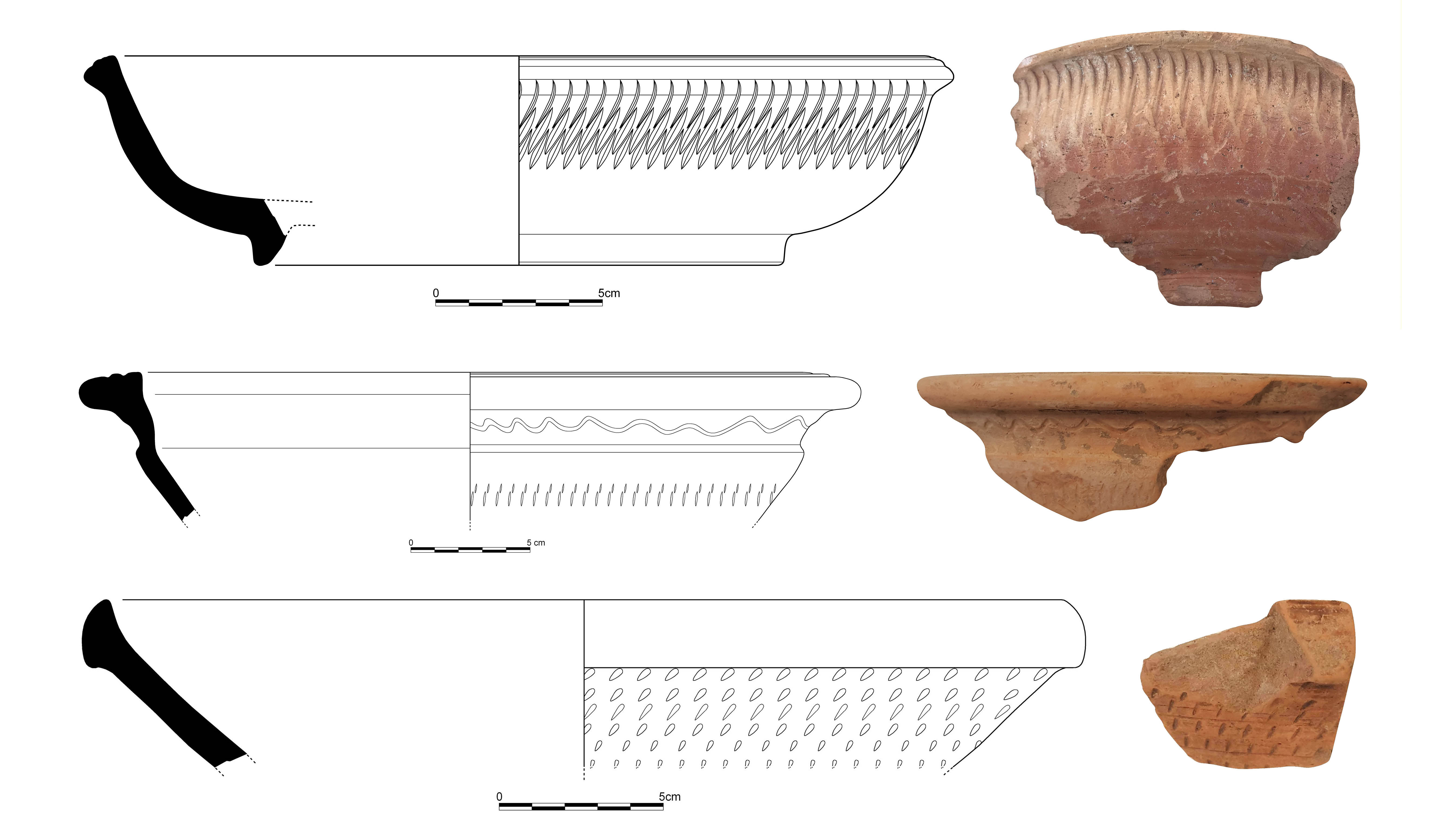
Preliminary Evaluations on Red Slipped Wares of Kepez Settlement Located in Sillyon Territorium
Mustafa BİLGİN
Abstract
Situated on a rocky hill in the Pamphylia Plain, the settlement of Kepez is located 4 km north of Sillyon, one of the important cities of the region, and with this feature it is considered to be a kome connected to Sillyon. Residential areas, workshops, necropolis, cisterns, water tanks and agricultural terraces identified in the settlement indicate that Kepez is a self-sufficient rural settlement. The density of red slipped ware detected in the surveys is also the data that supports this idea. In the surveys, among the red slipped wares, Eastern Sigillata D, dated to the Roman Imperial Period and Late Roman D Ware (LRD) dominating Mediterranean market in Late Antiquity were identified. Within the Eastern Sigillata D, there are three forms related to the typology of Hayes and early examples of these are dated to the 1st century AD. The most important evidence of the settlement related to the Late Antiquity is the red slipped wares known as Late Roman D Ware. Examples of different forms representing this period have been identified in Kepez. Of these, six forms are defined within the classification of Hayes. However, in Kepez, apart from these examples, the examples were also found that do not fit into Hayes classification but are associated with local production in some centers of Pamphylia and Pisidia. These have been described as different variations of the forms defined by Hayes as Late Roman D Ware. In this article, Eastern Sigillata D and Late Roman D Ware in Kepez will be promoted by examining and their dating suggestions will be shared with the world of science.
Adak-Adıbelli, I (2006). Tarsus Geç Roma Seramiği [Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi]. Ankara Üniversitesi.
Adamscheck, B. (1979). Kenchreai: The Pottery: Eastern Port of Corinth. Brill.
Alanyalı, H. S. (2011). Side 2010. ANMED, 19, 100-112.
Alanyalı, H. S. (2014). Side 2013 Yılı Kazı ve Araştırmaları. ANMED, 12, 94-108.
Alanyalı, H. S. (2016). Side 2015 Yılı Kazı ve Araştırmaları. ANMED, 14, 137-147.
Atik, N. (1995). Die Keramik aus den Südthermen von Perge. IstMitt-BH, 40. Verlag Ernst Wasmuth.
Bilgin, M., Kızıltepe-Bilgin, P. ve Özdemir, E. (2020). Yüzey Araştırmaları Işığında Sillyon Seramikleri Üzerine Ön Değerlendirmeler. M. Taşkıran (Ed.), Yüzey Araştırmaları Işığında Sillyon ve Çevresi, Sillyon Çalışmaları I (ss. 33-90). Ege Yayınları.
Daszewski, W. A., Majcherek, G., Sztetyllo, Z ve Zych, I. (1990). Excavations at Marina al-Alamein 1987-1988, MDIK, 46, 15-51.
Daszewski, W. A., Majcherek, G., Sztetyllo, Z. ve Zych, I. (1995). Cypriot Sigillata in Marina el-Alamein. H. Meyza ve J. Mlynarczyk (Eds.), Hellenistic and Roman Pottery in the Eastern Mediterranean – Advances in Scientific Studies, Acts of the II Nieborów Pottery Workshop 18-20 December 1993 (ss. 27-39). Research Center for Mediterranean Archaeology.
Diederichs, C. (1980). Céramiques Hellénistiques, Romaines et Byzantines, Salamine de Chypre IX. Diffusion de Boccard.
Eisenmenger. U. (2003). Late Roman Pottery in Limyra (Lycia). C. Abadie–Reynal (Ed.), Les céramiques en Anatolie aux Epoques Hellenistique et Romaine: Actes de la Table Ronde d’Istanbul, 22-24 mai 1996, Varia Anatolica XV, 193-196.
Ergürer, H. E. (2012). Parion Roma Dönemi Seramiği [Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi]. Atatürk Üniversitesi.
Ferrazzoli, A. F. (2003). Instrumentum domesticum. Tipologia dei reperti ceramici e aspetti delle produzioni e della circolazione dei materiali. E. E. Schneider (Ed.), Elaiussa Sebate II: Un Porto tra Oriente e Occidente (ss. 649-661). Roma: L’Erma di Bretschneider.
Fırat, N. (1999). Perge Konut Alanı Keramiği [Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi]. İstanbul Üniversitesi.
Fırat, N. (2000). So-called ”Cypriote Red Slip Ware” from the habitation area of Perge (Pamphylia). RCRFActa, 36, 35-38.
Fırat, N. (2003). Roman Period Ceramics. H. Abbasoğlu ve W. Martini (Eds.), Die Akropolis von Perge: Survey und Sondagen 1994−1997 (ss. 123-130). Philipp von Zabern.
Giudice, F., Pafumi, S. P., Malfitana, D., Sgarlata, M. ve Guzzetta, G. (1993). Paphos, Garrison’s Camp. Campagna 1989. RDAC, 279-327.
Giudice, F., Pafumi, S. P., Malfitana, D., Bruno, G. A. ve Guzzetta, G. (1994). Paphos, Garrison’s Camp. Campagna 1990. RDAC, 215-268.
Giudice, F., Oliveri, R. A., Pafumi, S. P., Privitera, A., Giudice, E., Malfitana, D., Narbone, G., Bruno, G. A. ve Guzzetta, G. (1996). Paphos, Garrison’s Camp. Campagna 1991. RDAC, 171-267.
Giudice, F., Giudice, G., Giudice, E., Guzzetta, G., Malfitana, D., Narbone, G., Oliveri, R. A., Privitera, A., Puppo, P. ve Rizzone, V. G. (1999). Paphos, Garrison’s Camp. VIa campagna. RDAC, 279-313.
Gunneweg, J. ve Perlman, I. ve Yellin, J. (1983). The Provenience, Typology and Chronology of Eastern Terra Sigillata, QEDEM, 17. Institute of Archaeology, Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Hayes, J. W. (1967). Cypriot Sigillata. RDAC, 65-77.
Hayes, J. W. (1972). Late Roman Pottery. British School at Rome.
Hayes, J. W. (1985). Sigillate Orientali. G. Pugliese-Carratelli (Ed.), Atlante delle Forme Ceramiche II. Ceramica Fine Romana nel Bacino Mediterraneo (Tardo Ellenismo e Primo Impero). Enciclopedia dell’arte antica classica e orientale (ss. 1-96). Istituto della Enciclopedia italiana.
Hayes, J. W. (1991). Paphos III: The Hellenistic and Roman Pottery. Department of Antiquities.
Hayes, J. W. (1994). Other Finewares. M. Fulford ve R. Tomber (Eds.), Excavations at Sabratha 1948-1951, Vol. II, The Finds. Part 2. The Finewares and Lamps (ss. 119-144). Libyan Department of Antiquities.
Hayes, J. W. (2008). Roman Pottery. Fine Ware Imports. Agora, XXXII, The American School of Classical Studies at Athens.
Jackson, M., Zelle, M., Vandeput, L. ve Köse, V. (2012). Primary Evidence for Late Roman D Ware Production in Southern Asia Minor: A Challenge ‘To Cypriot Red Slip Ware’, AnatSt, 62, 89-114. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0066154612000051
Jones, F. F. (1950). The Pottery. H. Goldman (Ed.), Excavations at Gözlü Kule, Tarsus. The Hellenistic and Roman Periods (ss. 149-296). Princeton University Press.
Kenkel, F. (2007). Cypriot Red Slip Ware and Its Derivatives from Pednelissos. B. Böhlendorf-Arslan, A. O. Uysal ve J. Witte-Orr (Eds.), Akdeniz ve Çevresindeki Arkeolojik Kazılarda Ele Geçen Geç Antik ve Ortaçağ Seramiği ve Mimari Seramiği, Byzas, 7 (ss. 131-146). Ege Yayınları.
Kenrick, P. M. (1981). Fine Ware of Hellenistic and Roman Periods. J. Matthers (Ed.), The River Qoueiq, Norhern Syria, and its Catchment. Studies Arising from the Tell Rifa’at Survey 1977-79. BAR International Series 98 (ss. 439-458). BAR Publishing.
Kenrick, P. M. (1985). Sidi Khrebish. Excavations at Sidi Khrebish Benghazi (Berenice) III(1): The Fine Pottery. Libya Antiqua, V. Department of Antiquities.
Kenyon, K. M. (1957). Terra Sigillata. J. W. Crowfoot, G. M. Crowfoot ve K. M. Kenyon (Eds.), Samaria-Sebaste 3: The Objects from Samaria (ss. 281-306). Palestine Exploration Fund.
Landgraf, J. (1980). Keisan’s Byzantine Pottery. J. Briend ve J. B. Humbert (Eds.), Tell Keisan (1971-1976): une cité phénicienne en Galilée (ss. 51-99). Vandenhoeck & Ruprech.
Lund, J. (1995). A Fresh Look at the Roman Fine Wares from the Danish Excavations at Hama, Syria. H. Meyza ve J. Mlynarczyk (Eds.), Hellenistic and Roman Pottery in the Eastern Mediterranean – Advances in Scientific Studies, Acts of the II Nieborów Pottery Workshop 18-20 December 1993 (ss. 135-161). Research Center for Mediterranean Archaeology.
Lund, J. (1997). The Distribution of Cypriot Sigillata as Evidence of Sea-trade involving Cyprus. S. Swiny, R. L. Hohlfelder ve H. Wylde-Swiny (Eds.), Res maritimae: Cyprus and the eastern Mediterranean from prehistory to late antiquity: proceedings of the Second International Symposium “Cities on the Sea”, Nicosia, Cyprus, October 18-22, 1994 (ss. 201-215). Scholars Press.
Magness, J. (1992). Late Roman and Byzantine Pottery, Preliminary Report, 1990. R. L. Vann (Ed.), Caesarea Papers: Straton’s Tower, Herod’s Harbour, and Roman and Byzantine Caesarea (ss. 129-153). Journal of Roman Archaeology.
McClellan, M. C. ve Rautman, M. L. (1994). The 1991–1993 Field Seasons at Kalavasos-Kopetra. RDAC, 289-308.
Meyza, H. (2007). NEA Paphos V: Cypriot Red Slip Ware. Studies on a Late Roman Levantine Fine Ware. Archeobooks.
Nahshoni, P. (1999). A Byzantine site in the Migdal Neigbourhood, Ashqelon, ‘Atiqot, 37, 99-111.
Oransay, B. S. A. (2012). Side 2009-2011 Yılı Kazılarında Ele Geçen Doğu Sigillatası D (Kıbrıs Sigillatası) Seramikleri. Anadolu/Anatolia, 28, 109-138. https://10.1501/andl_0000000396
Özdilek, B. (2018). Andriake Limanından Ele Geçen DSD Grubu/Kıbrıs Sigillataları Işığında Lykia’nın Doğu Akdeniz ile Deniz Ticareti. Phaselis, IV, 55-77. https://doi.org/10.18367/Pha.18004
Özer, E. (2012). 2010 Yılı Sillyon Antik Kenti ve Çevresi Yüzey Araştırması. Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, 29(3), 33-48.
Özer, E. ve Taşkıran, M. (2010a). Sillyon Antik Kenti ve Çevresi Yüzey Araştırması 2009. ANMED, 8, 165-169.
Özer, E. ve Taşkıran, M. (2010b). 2009 Yılı Sillyon Antik Kenti ve Çevresi Yüzey Araştırması. Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, 28(2) 279-296.
Poblome, J., Degryse, P., Cottica, D. ve Fırat, N. (2001). A New Early Byzantine Production Centre in Western Asia Minor. A Petrographical and Geochemical Study of Red Slip Ware From Hierapolis, Perge and Sagalassos. RCRFActa, 37, 119–126.
Poblome, J. ve Fırat, N. (2011). Late Roman D. A Matter of Open(ing) or Closed Horizons?. M. Cau, P. Reynolds, ve M. Bonifay (Eds.), LRFW 1. Late Roman Fine Wares. Solving problems of typology and chronology: A review of the evidence, debate and new contexts (ss. 49-56). Archaeopress.
Riley, J. A. (1975). The Pottery from the First Session of Excavations in the Caesarea Hippodrome, BASOR, 218, 25-63. https://doi.org/10.2307/1356166
Sackett, L. H. (1992). The Roman Pottery. L. H. Sackett (Ed.), Knossos from Greek City to Roman Colony. Excavations at the Unexplored Mansion II. BSA, Suppl. 21, 147-256.
Sion, O. (1997). Mishor Adummim (Khirbet Handoma). ‘Atiqot, 32, 149-158.
Slane, K. W. (1989). Corinthian Ceramic imports: the Changing Pattern of Provincial Trade in the First and Second Centuries A.D. S. Walker ve A. Cameron (Eds.), The Greeks Renaissance in the Roman Empire. Papers from the Tenth British Museum Classical (ss. 219-225). Oxford University Press.
Stepansky, Y. (1999). Two Mausolea on the Fringes of the Roman-Period Cemetery of Tiberias. ‘Atiqot, 37, 73-90.
Taşkıran, M. (2017). Sillyon Antik Kenti Savunma Sistemi ve Pamphylia Bölgesindeki Konumu [Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi]. Pamukkale Üniversitesi.
Taşkıran, M. (2020). Pamphylia Ovasında Bir Savunma Kenti: Sillyon. M. Taşkıran (Ed.), Yüzey Araştırmaları Işığında Sillyon ve Çevresi. Sillyon Çalışmaları I (ss. 1-30). Ege Yayınları.
Tekocak, M. (2006). Kelenderis Roma Çağı Seramiği [Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi]. Selçuk Üniversitesi.
Tekocak, M. (2007). Kelenderis Aşağı Şehir Sondajında Bulunan Kıbrıs Kırmızı Astarlı (Geç Roma D) Kapları. İDOL, 33, 16-25.
Tekocak, M. (2009). African and Cypriot Red slip wares from Kelenderis. H. Öniz (Ed.), Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on Mediterranean Archaeology (SOMA): Famagusta, North Cyprus, 5-8 March 2008. BAR International Series 2009 (ss. 132-142). Archaeopress.
Ustinova, Y. ve Nahshoni, P. (1994). Salvage Excavation in Ramat Nof, Be’er Sheva. ‘Atiqot, 25, 157-177.
Uygun, Ç. (2011). Patara IV.2. Tepecik Kırmızı Astarlı Seramikleri (İ.Ö. 2. yy – İ.S. 4. yy). Ege Yayınları.
Vandeput, L. (2009). Late Antiquity in the Taurus Mountains Remains in Pednelissos and its Territory. Colloquium Anatolicum, 8, 23-44.
Vandeput, L. ve Köse, V. (2010). Pisidia Survey Project: Research in the territorium of Pednelissos. Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, 27(2), 179–194.
Vandeput, L. ve Köse, V. (2013). Survey in the Taurus Mountain: Methodologies of the Psidia Survey Project. L. Lavan ve M. Mulryan (Eds.), Field Method’s and Post-Excavation Techniques in Late Antique Archaeology (ss. 205-248). Brill.
Vandeput, L., Köse, V. ve Jackson, M. (2011). Psidia Survey Project 2011: Research in the Territory of Pednelisos, Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, 28(3), 75-90.
Vapur, Ö. (2001). Roma Dönemi’nde Kırmızı Astarlı Bir Seramik Geleneği, I. Uluslararası Eskişehir Pişmiş Toprak Sempozyumu Bildiriler Kitabı (5 Ağustos-5 Eylül) (ss. 16-22). Eskişehir Tepebaşı Belediyesi.
Viaene, W., Poblome, J., Ottenburgs, R., Kucha, H., Hertongen, J. V. C., Waelkens, M. ve Laduron, D. (1995). Geochemical distribution of trace elements in Sagalassos Red Slip Ware. M. Waelkens ve J. Poblome (Eds.), Sagalassos III (ss. 245-270). Leuven University Press.
Waagé, F. O., (1948), Hellenistic and Roman Tableware of Nort Syria. F. O. Waage (Ed.), Antioch on the Orontes IV. 1: Ceramic and Islamic Coins (ss. 1–60). Princeton University Press.
Williams, C. (1989). Anemurium. The Roman and Early Byzantine Pottery. Pontificial Institute of Mediaeval Studies.
Yener-Marksteiner, B. (2020). Studien zum kaiserzeitlichen Tafelgeschirr aus Limyra. Forschungen in Limyra, 8. Verlag der österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften.
Yıldız, V. (2006). Tarsus Cumhuriyet Alanı Kazısında Bulunan Doğu Sigillataları A Grubu Seramikleri [Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi]. Selçuk Üniversitesi.
Yıldız, V. (2019). Soli Pompeiopolis Sütunlu Caddesi’nde Bulunan Doğu Sigillatası D Grubu Seramikleri. Selçuk Üniversitesi Fen Edebiyat Fakültesi Dergisi, 42, 245-274.
Yılmaz, Z. (2008). Die Keramik der späthellenistischen, kaiserzeitlichen, spätantiken und frühbyzantinischen Epochen (Ende 2. Jh. v. - 7. Jh. n. Chr.). F. Kolb (Ed.), Lykische Studien 8: Keramik, Münzen, Kirchen und Wirtschaftskomplexe des zentrallykischen Yavu-Berglandes (Gebiet von Kyaneai). Tübinger Althistorische Studien 4 (ss. 105-171). R. Habelt.
Zoroğlu, L. (1986). Samsat’da Bulunan Doğu Sigillitaları, İlk Rapor. S.Ü. Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi Edebiyat Dergisi, 3, 61-100.
Zoroğlu, L. (2003). Doğu Sigillataların İmalat Yerleri ve Dağılım Sorunu. C. Abadie-Reynal (Ed.), Les Ceramiques en Anatolia Aux Epoques Hellenistique Et Romaine. Varia Anatolica, XV, 121-123.
Bilgin, M. (2021). Sillyon Territoryumu’nda Bulunan Kepez Yerleşiminin Kırmızı Astarlı Seramikleri Üzerine Ön Değerlendirmeler. Arkhaia Anatolika, 4, 174-214. https://doi.org/10.32949/Arkhaia.2021.32