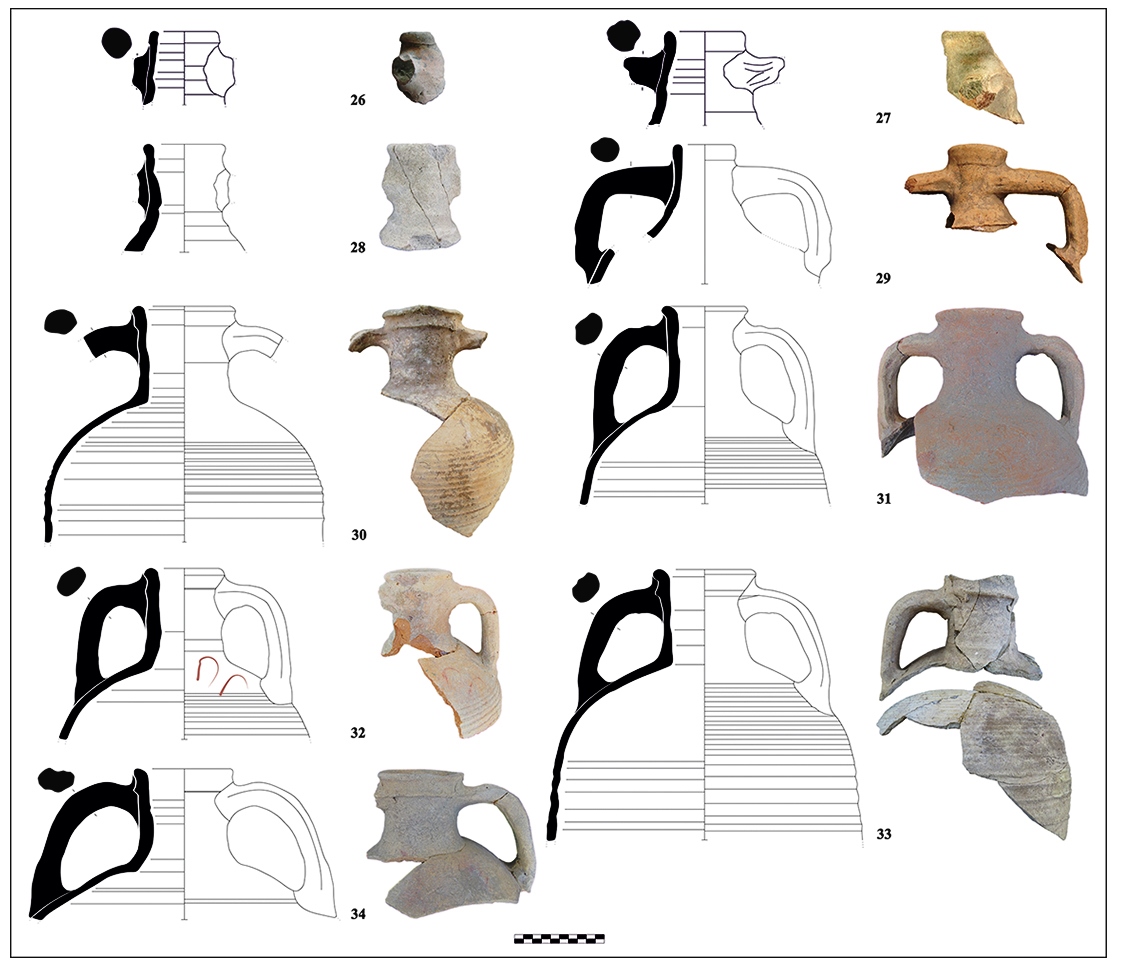
Parion Yamaç Hamamı Ticari Amphora Buluntuları (MÖ 1. yüzyıl - MS 7. yüzyıl)
İsmail AKKAŞ
Öz
Troas Bölgesi’nin kuzeyindeki Parion Antik Kenti, bugünkü Çanakkale ili, Biga ilçesi sınırları içerisindeki Kemer Köyü’nde yer almaktadır. Parion, coğrafi ve stratejik konumunun yanı sıra önemli bir ticaret limanına sahip olması gibi özellikleri sayesinde çağlar boyunca bölgedeki egemen güçlerin ilgisini çeken kentlerden biri olmuştur. MÖ 8. yüzyılda bir Grek kolonisi olarak kurulan Parion’a, Roma Cumhuriyet Dönemi sonlarında, Romalı emekli askerler yerleştirilmiş ve kente Roma kolonisi statüsü verilmiştir. Kentin bu statüsü ekonomik olarak da gelişmesini ve zenginleşmesini sağlamış, böylece Parion antik kenti Kuzey Troas Bölgesi’nde en fazla Romalı barındıran kentlerden biri olmuştur. Roma İmparatorluğu tarafından Roma koloni statüsü verilmesi sonrasında kent, gerek bölge ticaretinde, gerekse siyasi ve askeri alanlarda söz sahibi olmuştur. Bunun doğal bir sonucu olarak Parion’da 2005 yılından bu yana gerçekleştirilen kazılarda Roma Dönemi’ne ait önemli arkeolojik bulgulara ulaşılmıştır. Bu arkeolojik buluntu gruplarından biri de 2008-2019 yılları arası Yamaç Hamamı kazılarında ele geçen ticari amphora parçalarıdır. Çalışmamızda, yapıda bu yıllar arasında ele geçen Roma ve Erken Bizans Dönemi’ne ait ticari amphora buluntuları tanıtılmıştır. Bu dönemler içindeki tabaka ve kontekstlerde 18 farklı ithal amphora grubu tespit edilmiştir. Bu ticari amphora grupları İtalya, Kuzey Afrika (Tunus), Ege Adaları, Batı Anadolu, Güney Karadeniz, Kilikia ve Levant gibi önemli üretim merkezlerinden ithal edilmiştir. Parion Yamaç Hamamı’nda ele geçen ticari amphoralar, yapının inşa tarihi ve kullanım evrelerini desteklemesi açısından önemlidir. Çalışma kapsamında, Parion Yamaç Hamamı’nın MÖ 1. yüzyıl ortaları ile MS 7. yüzyılın ilk çeyreği arasına tarihlenen tabaka ve kontekstlerinde bulunan ticari amphoralar aracılığıyla hem yapıyla ilgili hem de ticari açıdan yeni verilere ulaşmak amaçlanmıştır.
Antik Kaynaklar
|
Pausanias |
Pausanias. Description of Greece: Vol. 1-5, (Çev. W. H. S. Jones), London-Cambridge, 1965. |
|
Strabon |
Strabon, Geographika: Antik Anadolu Coğrafyası, Kitap: XII-XIII-XIV, (Çev. A. Pekman), İstanbul, 2000. |
Modern Kaynaklar
|
Abadie-Reynal – Sodini 1992 |
C. Abadie-Reynal – J. P. Sodini, La céramique paléochrétienne de Thasos (Aliki, Delkos, fouilles anciennes. Etudes Thasiennes, XIII, Athènes, 1992. |
|
Abadie-Reynal 1989a |
C. Abadie-Reynal, “Céramique et Commerce dans le Bassin Égéen du IVe au VIIe Siècle”, Hommes et Richesses dans L’Empire Byzantin, Tome I, IVe -VIIe Siècle, Paris, 1989a, 143-162. |
|
Abadie-Reynal 1989b |
C. Abadie-Reynal, “Les Amphores Protobyzantines D’Argos (IVe-VIe siècles”, BCH, Supplément XVIII, Eds. V. Déroche – J. M. Spieser Recherches sur la Céramique Byzantine, Athenes, 1989b, 47-56. |
|
Açar 2017 |
E. Açar, Antandros Nekropolü Geç Roma Yerleşimi. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Ege Üniversitesi, İzmir, 2017. |
|
Adamsheck 1979 |
B. Adamsheck, Kenchreai, Eastern Port of Corinth, IV. The Pottery, Results of Investigations by The University of Chicago and Indiana University for The School of Classical Studies at Athens. Leiden, 1979. |
|
Akkaş 2020 |
İ. Akkaş, 2008-2019 Yılları Arası Amphora Buluntuları Işığında Parion Antik Kenti Roma ve Erken Bizans/Geç Roma Dönemi Ticari İlişkileri. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Mersin Üniversitesi, Mersin, 2020. |
|
Aktaş 2018 |
R. Aktaş, Antandros Kazısı Yamaç Ev Roma Dönemi Seramikleri. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Ege Üniversitesi, İzmir, 2018. |
|
Alexeeva 1997 |
E. M. Alexeeva, Antichnyiiy gorod Gorgippij. Moscow, 1997. |
|
Alkaç 2012 |
E. Alkaç, “Korykos (Kilikia) Yüzey Araştırmalarında Bulunan LR 1 Amphoraları”, Olba, XX (2012), 323-344. |
|
Alkaç 2013 |
E. Alkaç, “Silifke Müzesi’nden Doğu Akdeniz Üretimi Amphoralar”, Cedrus, I (2013), 107-124. |
|
Alpözen et al. 1995 |
T. O. Alpözen – H. Özdaş – B. Berkaya, Bodrum Sualtı Arkeoloji Müzesi Ticari Amphoraları, Bodrum, 1995. |
|
Amari 2006 |
S. Amari, 2006. “I materiali in esposizione nell’Antiquarium”, Sale I-II-III. Ed. M.G. Branciforti, L’area archeologica di Santa Venera al Pozzo-Acium. Antiquarium, Catania, Palermo, 2006, 105–183. |
|
Amari 2008 |
S. Amari, 2008. “A Late Roman Amphorae Production in Eastern Sicily”, Eds. O. Menozzi – M.L. Di Marzio – D. Fossataro. SOMA 2005: Proceedings of the IX Symposium on Mediterranean Archaeology, Chieti (Italy), 24-26 February 2005, Oxford, 2008, 473-479. |
|
Amari 2014 |
S. Amari, “Observations on the Late Roman Coarse Wares Production from the Factory of Acium in Sicily (Italy)”, LRCW, 4, 2014, 225-233. |
|
Anastasi 2019 |
M. Anastasi, Pottery from Roman Malta, Oxford, 2019. |
|
Anderson-Stojanovic 1992 |
V. R. Anderson-Stojanovic, Stobi, The Hellenistic and Roman Pottery, Oxford, 1992. |
|
Andronico 1991 |
E. Andronico, Il sito archeologico di Pellaro (fraz. di Reggio Calabria. Mélanges de l’École Française de Rome, Antiquitè, 103-102 (1991), 731–736. |
|
Arseneva – Böttger 1997 |
T. M. Arseneva – B. Böttger, “Griechen am Don. Die Grabungen in Tanais 1996“. Eurasia Ant. 3 (1997), 400-451. |
|
Arseneva – Naumenko 1992 |
T. Arseneva – S.A. Naumenko, Usad’by Tanaisa, Moscow, 1992. |
|
Arseneva – Naumenko 1995 |
T. Arseneva – S.A. Naumenko, Tanaïs IV-Ve s. Recueil Koselenko 1995: V Cest’60 - letija professora G.A. Koselenko [Recueil Bosporan en l’honneur des 60 ans du Professeur G.A. Koselenko], Bosporskij Sbornik 6 (1995), 45-58. |
|
Arthur 1985 |
P. Arthur, “Naples: Notes on the Economy of a Dark Age City”, Eds. C. Malone – S. Stoooart, Papers in Italian Archeology TV, pt. TV, Classical and Medieval Archaeology, BAR International Series 246, 1985, 247-259. |
|
Arthur 1989a |
P. Arthur, “Aspects of Byzantine Economy: An Evaluation of Amphora Evidence from Italy”, BCH Supplement, XVIII (1989), 81-91. |
|
Arthur 1989b |
P. Arthur, “Some Observations on the Economy of Bruttium under the later Roman Empire”, JRA, 2 (1989), 133-142. |
|
Arthur 1990 |
P. Arthur, “Anfore dall’alto Adriatico e il Problema del Samos Cistern type”, Aquileia Nostra Anno, LXI (1990), 282-294. |
|
Arthur 1998 |
P. Arthur, “Eastern Mediterranean amphorae between 500 and 700: A view from Italy”, Ed. L. Sagui, Ceramica in Italli: VI - VII secolo, Florence, 1998, 157-184. |
|
Asal 2010 |
R. Asal, Yenikapı Marmaray ve Metro Kurtarma Kazıları Buluntuları Işığında İstanbul’un Roma ve Bizans Dönemi Deniz Ticareti. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Trakya Üniversitesi, Edirne, 2010. |
|
Aubert 1996 |
C. Aubert, “Bey002. Rapportpreliminaire”, BAAL Bulletin d’Archéologie et d’Architecture du Liban, 1 (1996), 60-97. |
|
Aupert 1980 |
P. Aupert, “Objets de la vie quotidienne a Argos en 585 ap. J.- C”, BCH Suppl. 6 (1980), 395 - 457. |
|
Auriemma – Quiri 2004 |
R. Auriemma – E. Quiri, “Importazioni di anfore orientali nell’Adriatico tra primo e medio impero”, TATEM, 2004, 43-55. |
|
Avram 2004 |
A. Avram, The Propontic Coast of Asia Minor. Eds. M. H. Hansen – T. H. Nielsen, An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis, New York, 2004, 974-999. |
|
Aydın 2019 |
S. Aydın, Olba Geç Roma Dönemi Seramik Buluntuları. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Gazi Üniversitesi, Ankara, 2019. |
|
Badescu 2013 |
A. Badescu, “Amfore orientale de tip Kapitän II descoperite la Histria în Sectorul Basilica extra muros”, Materiale Şi Cercetări Arheologice Serie Nouă, IX (2013), 189-218. |
|
Bailey 1983 |
D. M. Bailey, “More Groups of Late Roman Pottery”, OP, 46 (2013), 26-52. |
|
Bailey 1991 |
D. M. Bailey, Excavations at El-Ashmunein IV, Hermopolis Magna: Buildings of the Roman Period, London, 1991. |
|
Bailey 1996 |
D. M. Bailey, “The Pottery from the South church at El-Ashmunein”, Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 4 (1996), 41-111. |
|
Bailey 1998 |
D. M. Bailey, Excavations at El-Ashmunein, V. Pottery, Lamps and Glass of the Late Roman and Early Arab Periods, Londra, 1998. |
|
Ballet – Dixneuf 2004 |
P. Ballet – D. Dixneuf, “Ateliers D’Amphores de la Chora Egyptienne aux Epoques Romaine et Byzantine”, TATEM, 2004, 67-72. |
|
Ballet – Picon 1987 |
P. Ballet – M. Picon, Recherches sur les origines, de la céramique des Kellia. Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 1 (1987), 17-48. |
|
Ballet 1997° |
P. Ballet “Tell al-Farama sud”, Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 5 (1997a), 123-127. |
|
Ballet 1997b |
P. Ballet “Teli al-Kana1s“, Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 5 (1997b), 129-132. |
|
Ballet 1998 |
P. Ballet “Les Ceramiques D’Alexandrie aux Periodes Hellenistique et Romaine”, Revue Archéologique, Nouvelle Série, Fasc. 1 (1998), 193-199. |
|
Ballet 2003 |
P. Ballet “La céramique. Contextes et Classification”, Eds. P. Ballet – M. Rassart – Debergh – N. Bosson, Kellia II. L’ermitage copte QR 195. 2. La céramique, les inscriptions, les décors, Caire, 2003, 1-107. |
|
Bass – Van-Doorninck 1971 |
G. F. Bass – F. H. Van-Doorninck, “A Fourth-Century Shipwreck at Yassi Ada”, AJA, 75 (1) (1971), 27-37. |
|
Bass – Van-Doorninck 1982 |
G. F. Bass – F. H. Van-Doorninck, Yassi Ada, I, A Seventh-Century Byzantine Shipwreck, Texas, 1982. |
|
Bass 1982 |
G. F. Bass, “The Pottery”. Eds. G. F. Bass – F. H. Van-Doorninck, Yassı Ada Vol. I. A Seventh-Century Byzantine Shipwreck, Texas, 1982, 155-188. |
|
Başaran – Ergürer 2012 |
C. Başaran – H. E. Ergürer, “Parion Odeion’u (Bouleuterion?) 2010 Çalışmaları ve Odeion’da Bulunan Seramikler“, Olba, XX (2012), 245-289. |
|
Başaran 1999 |
C. Başaran, “Parion 1997 Araştırmaları”, XVI. Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, Ankara, 1999, 349-364. |
|
Başaran 2002 |
C. Başaran, Geçmişten Günümüze Bayramiç, Tarihi - Coğrafyası ve Arkeolojisi, Ankara, 2002. |
|
Başaran 2006 |
C. Başaran, “Parion: Karanlıktan Gün Işığına“. Ed. T. Takaoğlu, Anadolu Arkeolojisine Katkılar 65. Yaşında Abdullah Yaylalı’ya Sunulan Yazılar, İstanbul, 2006, 185-200. |
|
Başaran 2008 |
C. Başaran, “Parion’dan Persia’ya Yol Gider, Euergetes”, Prof. Dr. Haluk Abbasoğlu’na 65. Yaş Armağanı Cilt I, İstanbul, 2008, 133-137. |
|
Başaran 2010 |
C. Başaran, “Parion 2008 Kazıları”, 31. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, Ankara, 2010, 393-410. |
|
Başaran 2011 |
C. Başaran, “Parion 2009 Yılı Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları”, 32. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, Ankara, 2011, 283- 300. |
|
Başaran et al. 2013 |
C. Başaran – V. Keleş – H. Kasapoğlu – H. E. Ergürer, “Parion 2011 Kazıları”, 34. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, II. Cilt, Ankara, 2013, 347-364. |
|
Başdemir 2019 |
B. Başdemir, Troas Bölgesi Buluntusu Ticari Amphoralar: Tipolojik ve Fonksiyonel Bir Analiz. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart Üniversitesi, Çanakkale, 2019. |
|
Ben Abed-Ben Khader et al. 2000 |
A. Ben Abed-Ben Khader – M. Bonifay – G. Filantropi, F. Giomblanco – M. Griesheimer – M. Larcher – J.-Ch. Treglia, “Une sépulture romaine tardive en milieu rural (Jebel Harboun, région d’Hammamet, Tunisie) ”, Antiquités Africaines 36 (2000), 137-146. |
|
Benea 1996 |
D. Benea, Dacia sud – vestică în secolele III–IV, Timişoara, 1996. |
|
Benea 2000 |
D. Benea, “Les amphores de Tibiscum. Les relations commerciales entre la Dacie et les territoires de la Méditerranée orientale”, RCRF Acta 36, 2000, 435 –438. |
|
Berndt 2003 |
M. Berndt, Funde aus dem Survey auf der halbinsel von Milet 1992-1999) Kaiserzeitliche und frühbyzantinische Keramik. Internationale Archäologie 79, Rahden, 2003. |
|
Bezeczky 1987 |
T. Bezeczky, Roman Amphorae from the Amber Route in Western Pannonia, BAR International Series 386, Oxford, 1987. |
|
Bezeczky 2004 |
T. Bezeczky, “Early Roman Food Import in Ephesus: Amphorae from the Tetragonos Agora”, TATEM, 2004, 85-97. |
|
Bezeczky 2005 |
T. Bezeczky, “Late Roman amphorae from the Tetragonos-Agora in Ephesus”, Ed. F. Krinzinger, Spatantike und Mittelalterliche Keramik aus Ephesos Archaologische Forschungen, Band 13 (2005), 203-230. |
|
Bezeczky 2006 |
T. Bezeczky, “Consumer Behaviour in Ephesus in the first century BC”, Eds. D. Malfitana – J. Poblome – J. Lund, Old Pottery in a New Century, Innovating Perspectives on Roman Pottery Studies, Catania, 2006, 287-308. |
|
Bezeczky 2008 |
T. Bezeczky, “Italian Wine in the Eastern Mediterranean. Amphorae from Etruria, Latium, and Campania from the fourth century B.C. to the first century A.D. The Case of the Ephesian Amphorae”, Bollettino di Archeologia on Line, Volume Speciale, International Congress of Classical Archaeology Meetings Between Cultures in the Ancient Mediterranean, Roma, 2008, 82-92. |
|
Bezeczky 2010 |
T. Bezeczky, “Trade Connections between Ephesus and Adriatic Region”, Histria Antiqua, 19 (2010), 351-358. |
|
Bezeczky 2012 |
T. Bezeczky, “Roman Amphorae in Ephesus“. Forum Archaeologiae Zeitschrift für Klassische Archaeologie, 62 (III) (2012), 1-8. |
|
Bezeczky 2013 |
T. Bezeczky, The Amphorae of Roman Ephesus, Ephesos XV/I. Wien, 2013. |
|
Bien 2005 |
S. Bien, Des Niveaux du VII e Siècle Sous le Music-Hall del L’Alcazar à Marseille”, LRCW, 1, 2005, 285-298. |
|
Blakely 1987 |
J. A. Blakely, The Joint Expedition to Caesarea Maritinıa, Excavations Report. The Potte1y and Dating of Vault I: Horreum, Mithraeum and Later Uses. The Joint Expedition to Caesarea Maritima Excavations Reports. 4. ASOR Excavations Reports, 1987. |
|
Bonifay – Pieri 1995 |
M. Bonifay – D. Pieri, “Amphores du Ve au VIIe s. à Marseille: nouvelles données sur la typologie et le contenu“. JRA, 8 (1995), 94-120. |
|
Bonifay – Reynaud 2004 |
M. Bonifay – P. Reynaud, “La céramique de la basilique méridionale”. Eds. A. Ben Abed-Ben Khader – M. Fixot – M. Bonifay – S. Roucole, Sidi Jdidi I: la basilique sud. Coll. de l’EFR, 339, Rome, 2004, 229-316. |
|
Bonifay – Villedieu 1989 |
M. Bonifay – F. Villedieu, “Importations d’amphores orientales en Gaule (V e – VII e siècle“. Eds. V. Déroche – J. M. Speiser, Recherches sur la céramique Byzantine, Oxford, 1989, 17-46. |
|
Bonifay 1986 |
M. Bonifay, “Observations Sur les Amphores Tardives à Marseille D’Après les Fouilles de la Bourse 1980-1984)”, Revue Archéologique de Narbonnaise, 19, 1986, 269-305. |
|
Bonifay 2002 |
M. Bonifay, “Les ultimes niveaux d’occupation de Sidi Jdidi, Pupput et Neapolis: difficultés de datation par la céramique, 2002”, L’Afrique vandale et byzantine. Actes du colloque international (Tunis, 5-8 octobre 2000), Antiquité Tardive, 10 (2002, 182-190. |
|
Bonifay 2004a |
M. Bonifay, Observations préliminaires sur la céramique de la nécropole de Pupput. Griesheimer, 2004a. |
|
Bonifay 2004b |
M. Bonifay, Études sur la céramique romaine tardive d’Afrique. British Archaeological Reports International Series 1301, Oxford, 2004b. |
|
Bonifay et al. 1989 |
M. Bonifay – G. Congès – M. Leguilloux, “Amphores tardives (Ve- VIIe siècle) à Arles et à Marseille”, Rome: École Française de Rome, 114 (1989), 1-2. |
|
Bonifay et al. 2001 |
M. Bonifay – R. Leffy – C. Capelli – D. Pieri, “Les céramiques du remplissage de la citerne du Sarapeion a Alexandrie”, Alexandrina II (2001), 39-84. |
|
Bonifay et al. 2002/03 |
M. Bonifay – C. Capelli – T. Martin – M. Picon – L. Vallauri, “Le littoral de la Tunisie: étude géoarchéologiq ue et historique 1987-1997): la céramique”, Antiquités Africaines, 38-39 (2002-2003), 125-202. |
|
Bruno 1989 |
B. Bruno, “Lombardia: Ricerche in Corso”, Amphores Romaines et Histoire Economique (A.R.H.E.), Collection de L’Ecole Française de Rome 114 (1) (1989), 642-644. |
|
Bruno 1997 |
B. Bruno, “Contenitori da transporto: i consumi di olio, vino e di altre derrate”, Ed. F. Filippi, Alba Pompeia, Archaeologia della citta dalla fondazione alla tarda antichita, Alba, 1997, 526-550. |
|
Bushi – Xhaferaj 2018 |
S. Bushi – E. Xhaferaj, “VIIth Century African Amphorae in Albania”, Eds. J. L. Lamboley – L. Përzhita – A. Skenderaj, Actes du VIe colloque international de Tirana 20-30 mai 2015) L’Illyrie méridionale et l’Épire dans l’Antiquité – VI, Paris, 2018, 907-911. |
|
Bushi 2016 |
S. Bushi, Amforat e Antikitetit të Vonë në Shqipëri (Shek. IV – VII M. KR.), Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Albanolojik Araştırmalar Merkezi (Center for Albanian Studies), Albania, 2016. |
|
Cambitoglou – Papadopoulos 1991 |
A. Cambitoglou – J. Papadopoulos, “Excavations at Torone”, Mediterranean Archaeology, 4 (1991), 147-171. |
|
Capelli 1998 |
C. Capelli, “Analisi minero-petrografiche“. Ed. L. Sagui, Ceramica in Italia: VI–VII secolo, Atti del Convegno in onore di John W. Hayes (11–13 May, 1995, Rome), Firenze, 1998, 331-337. |
|
Carboni 2010 |
F. Carboni, “Roma: un contesto anfbrico di V secolo da un ambiente della Domus Tiberiana sul Palatino”, LRCW, 3, 2010, 417-426. |
|
Carignani – Pacetti 1989 |
A. Carignani – F. Pacetti, “Le Importazioni di Anfore Bizantine a Roma fra IV e V Secolo: Le Evidenze di Alcuni Contesti Urbani”, Eds. V. Déroche – J. M. Spieser, Recherches sur la Céramique Byzantine, BCH Suppl XVIII, Oxford, 1989, 5-16. |
|
Carredano et al. 2007 |
A. F. Carredano – E. Garcia-Vargas, D. Gonzalez-Acuna, “Ánforas tardoantiguas en Hispalis (Sevilla, España) y el comercio mediterráneo”, LRCW, 2 (I), 2007, 133-146. |
|
Celuzza – Rendini 1992 |
M. Celuzza – P. Rendini, Relitti di storia : archeologia subacquea in Maremma, Sienne, 1992, 106-134. |
|
Cirelli 2007 |
E. Cirelli, “Ravenna e il commercio nell’Adriatico in età tardoantica”, Eds. A. Augenti – C. Bertelli, Felix Ravenna. La croce, la spada, la vela: l’alto Adriatico tra V e VI secolo, Catalogo della Mostra (Ravenna, 10 marzo-7 ottobre 2007), Milano, 2007, 45-50. |
|
Corti 2005 |
C. Corti, “Anfore e Ceramiche D’Impasto Grezzo dal Sito Corte Vanina (Concordia Sulla Secchia/Modena/Italia): Importazioni e Produzioni Locali tra Tardoantico e Altomedioevo”, LRCW, 1, 2005, 355-367. |
|
Costantini 2011 |
A. Costantini, “Le Anfore”, Eds. A. Alberti – E. Paribeni, Archeologia in Piazza dei Miracoli, Gli Scavi 2003-2009, Madrid, 2011, 393-430. |
|
Costantini 2014 |
A. Costantini, “Pisa: importazioni tra tarda antichità e altomedioevo da Piazza Duomo”, LRCW, 4 (I), 2014, 985-992. |
|
Çelikbaş – Oyarçin 2014 |
E. Çelikbaş – K. Oyarçin, “Parion Yamaç Hamamı”, Tarih Kültür ve Sanat Araştırmaları Dergisi, 3 (4) (2014), 61-85. |
|
Çelikbaş 2010 |
E. Çelikbaş, Parion Roma Kolanizasyon Sikkeleri. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Atatürk Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2010. |
|
Çelikbaş 2013a |
E. Çelikbaş, “Yamaç Hamamı”, Ed. C. Başaran, Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti, Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 67-76. |
|
Çelikbaş 2013b |
E. Çelikbaş, “Parion Yayınları”, Ed. C. Başaran, Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti, Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 215-219. |
|
Çelikbaş 2015 |
E. Çelikbaş, “Parion’dan Bir Trapezophoros = Masa Ayağı”, Eds. C. Başaran – V. Keleş, Parion Kazıları 10. Yıl Armağanı, Ankara, 2015, 43-48. |
|
Çelikbaş 2016 |
E. Çelikbaş, 2005-2014 Parion Kazısı Metal (Bronz-Demir-Kurşun) Buluntuları. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Atatürk Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2016. |
|
Çibuk 2019 |
K. Çibuk, Kocaeli Müzesi Amphora Koleksiyonu. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Kocaeli, 2019. |
|
Daszkiewicz et al. 2000 |
M. Daszkiewicz – E. Bobryk – G. Schneider – P. Dyczek, “Chemical and mineralogical composition of Roman amphorae from Novae and some other sites in Bulgaria, first results”, Novensia, 12 (2000), 23-41. |
|
Demesticha 2000 |
S. Demesticha, “The Paphos Kiln: Manufacturing Techniques of LR 1 Amphoras”, RCRF, Acta 36, 2000, 549-554. |
|
Demesticha 2003 |
S. Demesticha, “Amphora productions on Cyprus during the late Roman period”, Ed. C. Bakirtzes, VIIe congrés international sur la céramique médiévale en méditeranée, Thessaloniki, 11-16 Octobre 1999, Athènes, 2003, 469-476. |
|
Didioumi 2011 |
S. Didioumi, “Νεότερα ευρήματα για την πρωτοβυζαντινή Κω από τις σωστικές ανασκαφές στο νησί”, Eds. I. Baldini – M. Livadiotti, Archeologia protobizantina a Kos. La basilica di S. Gabriele, Universita di Bologna, Studi e Scavi NS 28, Bologna, 2011, 87-115. |
|
Didioumi 2014 |
S. Didioumi, “Local Pottery Production in the Island of Cos, Greece from the Early Byzantine Period. A Preliminary Report”, LRCW 4 (I), 2014, 169-180. |
|
Diederichs 1980 |
C. Diederichs, Salamine de Chypre. IX. Ceramiques hellenistiques, romaines et byzantines. Paris, 1980. |
|
Dixneuf 2011 |
D. Dixneuf, Amphores égyptiennes. Productions, typologie, contenu et diffusion (3e siècle avant J.-C. – 9e siècle après J.-C. Études Alexandrines 22, Alexandria, 2011. |
|
Doksanaltı 2020 |
E. M. Doksanaltı, “Knidos ‘Liman Caddesi’ Geç Antik Dönem Atölye/Dükkân ve Buluntuları”, Olba XXVIII (2020), 377-420. |
|
Dressel 1879 |
H. Dressel, “Di un grande deposito di anfore rinvenuto nel moro quartiere del Castro Pretorio”, Bulletino della Comissione Archaeologica Communale di. Roma 7, (1879), 36-112, 143-196. |
|
Dressel 1899 |
H. Dressel, Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum, Vol. XV, Berlin, 1899. |
|
Dündar 2012 |
E. Dündar, “A Group of Amphorae from Side Museum and a New Type of Amphora The Lycian Amphora”, Archäologischer Anzeiger, 2012 (1), 43-61. |
|
Dündar 2018 |
E. Dündar, “Maritame Trade of Roman Patara. Priliminary Remarks on the Amphorae”, Skyllis, 18/2 (2018), 166–173. |
|
Dyczek 2001 |
P. Dyczek, Roman amphorae of the 1st-3rd centuries AD found on the Lower Danube. Typology, Warsaw, 2001. |
|
Dyczek 2007 |
P. Dyczek, “Late Roman amphorae from the site of valetudinarium at Novae”, LRCW, 2 (2), 2007, 827-834. |
|
Dyczek 2010 |
P. Dyczek, “Kapitän II amphorae from Novae—between East and West”, LRCW 3 (II), 2010, 993–999. |
|
Egloff 1977 |
M. Egloff, “La potterie copte. Quatre siècles d’artisanat et d’échanges en basse- Égypte“. Kellia III (1977), 108-119. |
|
Ehmig 2002 |
U. Ehmig, “Deux assainissements avec amphores à Mayence (Germanie supérieure)”, Gallia, 59 (2002), 233-251. |
|
Eiwanger 1981 |
J. Eiwanger, Demetrias IV, Keramik und Kleinfunde aus der Damokratia - Basilika in Demetrias, Die Deutschen Archäologischen Forschungen in Thessalien, Bonn, 1981. |
|
Empereur – Picon 1986 |
J. Y. Empereur – M. Picon, “ À la recherche des fours d’amphores. ”, BCH Supplement XIII (1986), 103-126. |
|
Empereur – Picon 1989 |
J. Y. Empereur – M. Picon, “Les régions de production d’amphores impériales en Méditerranée orientale”, Amphores romaines et histoire économique : dix ans de recherche. Actes du colloque de Sienne, 22-24 mai 1986, organisé par l’Università degli studi di Siena, l’Università degli studi di Roma-La Sapienza, le Centre national de la recherche scientifique (RCP 403) et l’École française de Rome. Rome, 1989, 223-248. |
|
Empereur – Picon 1992 |
J. Y. Empereur – M. Picon, “La reconnaissance des productions des ateliers ceramiques: l’exemple de la Mareotide”, Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 3 (1992), 145-152. |
|
Empereur – Picon 1998 |
J. Y. Empereur – M. Picon, “Les Ateliers d’amphores du Lac Mariout”, BCH Supplement, 33 (1998), 75-99. |
|
Empereur et al. 1991 |
J. Y. Empereur – C. Kritzas – A. Marangou-Lerat, “À la recherche des ateliers d’amphores en Crète centrale”, BCH Supplement, 115 (1991), 481-523. |
|
Engemann 1992 |
J. Engemann, “A Propos des Amphores d’Abou Mina”, Cahiers de la Céramique Egyptienne 3, 153-159. |
|
Ergürer 2012 |
H. E. Ergürer, Parion Roma Dönemi Seramiği. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Atatürk Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2012. |
|
Ergürer 2013 |
H. E. Ergürer, “Seramikler”, Ed. C. Başaran, Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti, Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013 137-150. |
|
Erten et al. 2004 |
H. N. Erten – D. Kassab-Tezgör – I. R. Türkmen – A. Zararsız, “The Typology and Trade of the Amphorae of Sinope. Archaeological Study and Scientific Analyses”, TATEM, 2004, 103-115. |
|
Ferrazzoli – Ricci 2009 |
A. F. Ferrazzoli – M. Ricci, “Cilician Ceramic Production from Roman to Byzantine Age. New Data from Elaiussa Sebaste”, Olba, XVII (2009), 33-44. |
|
Ferrazzoli – Ricci 2010 |
A. F. Ferrazzoli – M. Ricci, “Un Centro di Produzione delle Anfore LR 1: Elaiussa Sebaste in Cilicia. Gli Impianti, Le Anfore”, LRCW, 3 (II), 2010, 815-819. |
|
Fırat 2018 |
G. Fırat, Parion Yamaç Hamamı 1515-1260 Sektörü Hellenistik Dönem Seramikleri. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Ondokuz Mayıs Üniversitesi, Samsun, 2018. |
|
Fırat 2019 |
M. Fırat, “Phokaia Mozaikler Alanı’nda Ele Geçen Roma Dönemi Amphoraları”, Seramik Araştırmaları Dergisi, 1 (2019), 30-53. |
|
Franco – Capelli 2014 |
C. Franco – C. Capelli, “New archaeological and archaeometric data on wine Sicilian amphorae in the Roman period (1st to 6th century AD): typology, origin and distribution in selected western Mediterranean contexts”, RCRF Acta, 43, 2014, 547-555. |
|
Franco 2012 |
P. Franco, African Amphorae from Portus. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Southampton Üniversitesi, Southampton, 2012. |
|
Franco 2014 |
C. Franco, Sicilian Amphorae (1st–6th centuries AD): Typology, Production and Trade. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Oxford Üniversitesi, Oxford, 2014. |
|
Freed 1995 |
J. Freed, “The Late Series of Tunisian Cylindrical Amphoras at Carthage”, JRA, 8 (1995), 155-191. |
|
Freed 2000 |
J. Freed, “Adoption of the Form of the Koan Amphora to the Production of ‘Dressel 24’ Amphoras in Italy and Northeastern Spain”, RCRF Acta, 36, 2000, 459-466. |
|
Frisch 1983 |
P. Frisch, Die Inschriften von Parion. Inschriften Griecuscher Städte aus Kleinasien, 25, Bonn, 1983. |
|
Fulford – Peacock 1984 |
M. G. Fulford – D. P. S. Peacock, Excavations at Carthage, The British Mission, I, 2, The Avenue du Président Habib Bourguiba, Salammbô: The Pottery and other Ceramic Objects from the Site, Sheffield, 1984. |
|
Gallimore 2011 |
S. C. Gallimore, An Island Economy: Ierapetra and Crete in the Roman Empire. Dissertation, University at Buffalo, State University of New York, 2011. |
|
Gandolfi et al. 2010 |
D. Gandolfi – G. Murialdo – C. Capelli – M. Bonifay, “Anfore africane di tardo v-vii secolo in Liguria (Italia): un aggiornamento dei dati archeologici e archeometrici”, LRCW, 3 (1), 2010, 33-56. |
|
Gantes – Moliner 1990 |
L. F. Gantes – M. Moliner, “Marseille (Massalia. Quartier Sainte-Barbe: îlot Puget III”, Eds. J.P. Jacob – A. D’anna, Informations archéologiques Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur Marsilya, 1990, 1-172. |
|
Garcia-Vargas 2011 |
E. Garcia-Vargas, “Oriental trade in the Iberian Peninsula during late antiquity (4-7 centuries AD): An archaeological perspective”, Ed. D. H. Lafuente, New perspectives on the late Antiquity, Cambridge, 2011, 76-117. |
|
Gassner 2011 |
V. Gassner, “Amphora Production in Calabria”, Kaynak: http://facem.at/ims/pdf/ Amphorae Production in Calabria 06 06 2011.pdf. |
|
Ghalia et al. 2005 |
T. Ghalia – M. Bonifay – C. Capelli, “L’atelier de Sidi-Zahruni: Misse en Evidence d’une Production d’amphores de l’antiquité Tardive sur le Territoire de la Cité de neapolis (Nabeul, Tunusie)”, LRCW, 1, 2005, 495-507. |
|
Goldman 1950 |
H. Goldman, Excavation at Gözlükule, Tarsus, Volume I - II, The Hellenistic and Roman Periods, New Jersey, 1950. |
|
Grelle – Volpe 1994 |
F. Grelle – G. Volpe, “La geografia amministrativa ed economica della Puglia tardoantica”, Eds. C. Carletti – G. Otranto, Atti del Convegno Internazionale Culto e insediamenti micaelici nell’Italia meridionale fra tarda antichità e medioevo (Monte Sant’Angelo 1992), Bari, 1994, 15-81. |
|
Gülsefa 2015 |
G. Gülsefa, 2006-2013 Myndos Kazılarında Ele Geçen Amphoralar ve Amphora Mühür Buluntuları. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Uludağ Üniversitesi, Bursa, 2015. |
|
Gürbüzer 2018 |
M. Gürbüzer, “Late Roman Pottery from a Building in Klazomenai”, Olba, XXVI (2018), 123-176. |
|
Hammond 2015 |
M. D. Hammond, Late Roman Ceramics from the Panayia Field, Corinth (Late 4th to 7th c.): The Long-Distance, Regional and Local Wares in Their Economic, Social and Historical Contexts, Missouri, 2015. |
|
Hayes 1983 |
J. W. Hayes, “The Villa Dionysos Excavations, Knossos: The Pottery”, BSA 78 (1983), 97-172. |
|
Hayes 1991 |
J. W. Hayes, “Commercial Amphorae: Hellenistic Types, Roman Types”, The Hellenistic and Roman Pottery, PAPHOS, Vol. III, Nicosia, 1991, 58-223. |
|
Hayes 1992 |
J. W. Hayes, Excavations at Saraçhane in Istanbul: Vol. 2. Princeton, 1992. |
|
Hayes 2003 |
J. W. Hayes, “Hellenistic and Roman Pottery Deposits from the ‘Saranda Kolones’ Castle Site at Paphos”, BSA 98 (2003), 447-516. |
|
Hayes 2007 |
J. W. Hayes, “Pottery”, Ed. A. H. Megaw, Kourion. Excavations in the Episcopal Precinct, Washington, 2007, 435-476. |
|
Heath – Tekkök 2007/08 |
S. Heath – B. Tekkök, “Greek, Roman and Byzantine Pottery at ilion (Troia 2007-2008 Project Troia)” Kaynak: http://classiscs.uc.edu/troy/grbpottery. |
|
Hesein 2014 |
M. A. H. Hesein, Bridging the Eastern and Western Mediterranean: The Roman Harbour Sites on the Coast of Cyrenaica, North-Eastern Libya. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Leicester Üniversitesi, Leicester, 2014. |
|
Hesnard 1980 |
A. Hesnard, “Un Depot Augusteen D’Amphores a la Longarina, Ostie (An Augustan Deposit of Amphoras at la Longarina, Ostia”, Memoirs of the American Academy in Rome Vol. 36, The Seaborne Commerce of Ancient Rome: Studies in Archaeology and History, 1980, 141-156. |
|
Hobson 2012 |
M. Hobson, The North African Boom: Evaluating Economic Growth in the Roman Province of Africa Proconsularis (146 B.C. - 439 A.D.), JRA Supplementary Series 100, Portsmouth, 2012. |
|
Hoxha 2003 |
G. Hoxha, Scodra dhe Praevalis në Antikitetin e Vonë, Shkodër, 2003. |
|
Iavarone – Olcese 2013 |
S. Iavarone – G. Olcese, “Le anfore Dressel 2-4 di Produzione Tirrenica: una Proposta di Progetto Archeologico ed Archeometrico”, Ed. G. Olcese, Immensa Aequora Workshop Ricerche archeologiche, archeometriche e informatiche per la ricostruzione dell’economia e dei commerci nel bacino occidentale del Mediterraneo (metà IV sec. a.C. - I sec. d.C.) A’i del convegno Roma 24-26 gennaio 2011, Roma, 2013, 221-226. |
|
Johnson 1986 |
B. L. Johnson, “Syro-Palestinian Bag-Shaped Amphoras in the Athenian Agora and Corinth Collections”, Eds. J. -Y. Empereur – Y. Garlan. Recherches sur les amphores grecques, BCH Suppl. XIII, Oxford, 1986, 589-597. |
|
Johnson 2008 |
B. L. Johnson, Ashkelon 2: Imported Pottery of the Roman and Late Roman Periods, Eisenbrauns, 2008. |
|
Joncheray 1975a |
J. P. Joncheray, “L’épave «E» du cap Dramont, sigillée claire D et amphores rescapées du pillage”, Cahiers d’Archéologie Subaquatique, IV (1975), 141-146. |
|
Joncheray 1975b |
J. P. Joncheray, “Une épave du Bas- Empire: Dramont F”, Cahiers d’Archéologie Subaquatique, IV (1975b), 92-132. |
|
Joncheray 1997 |
J. P. Joncheray, “Deux épaves du bas-empire romain, Deuxieme partie: L’épave Héliopolis 1”, Chaiers d’archaeologie Subaquatique, 13 (1997), 137-154. |
|
Kapitän 1972 |
G. Kapitän, “Le anfore del relitto romano dia capo Ognina, Siracusa”, Recherches sur les amphores romaines, Collection de l’ecole Française de Rome, 10 (1972), 243-252. |
|
Karagiorgou 2001 |
O. Karagiorgou, “LRA2: a container from the military annona on the Danubian border?”, Eds. S. Kingsley – M. Decker. Economy and Exchange in the East Mediterranean during Late Antiquity, Oxford, 2001, 129-166. |
|
Karagiorgou 2009 |
O. Karagiorgou, “Mapping Trade by the Amphora, Byzantine Trade, 4th-12th Centuries: The Archaeology of Local, Regional, and International Exchange”, Ed. M. M. Mango. Papers of the Thirty-eighth Spring Symposium of Byzantine Studies (St. John’s College, University of Oxford, March 2004), Society for the Promotion of Byzantine Studies Publications 14, Oxford, 2009, 37-58. |
|
Karcı-Ağlar 2015 |
G. Karcı-Ağlar, Smyrna Agorası’nda EIe Geçen Ticari Amphoralar 1998-2006 KazıIarı. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi, İzmir, 2015. |
|
Kasapoğlu – Özdemir 2013 |
H. Kasapoğlu – S. Özdemir, “Cam Eserler“, Ed. C. Başaran. Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti: Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 151-165. |
|
Kasapoğlu 2013a |
H. Kasapoğlu, “Metal Eserler“, Ed. C. Başaran. Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti: Parion, 1997- 2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 165-171. |
|
Kasapoğlu 2013b |
H. Kasapoğlu, “Kemik Objeler”, Ed. C. Başaran. Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti: Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 171-177. |
|
Kasapoğlu 2013c |
H. Kasapoğlu, “Heykelcik ve Figürinler“, Ed. C. Başaran. Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti: Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 177-193. |
|
Kasapoğlu 2015 |
H. Kasapoğlu, Parion Roma Dönemi Terrakotta Figürinleri 2004-2013. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Atatürk Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2015. |
|
Kasapoğlu et al. 2020 |
H. Kasapoğlu – V. Keleş – G. Fırat, “Parion Yamaç Hamamı 1515-1260 Depoziti Batı Yamacı Seramikleri”, Turkish Studies - History, 15 (1) (2020), 91-122. |
|
Kassab-Tezgör 2009 |
D. Kassab-Tezgör, Les Fouılles et le Materiel de l’Atelier Amphorıque de Demirci Pred de Sinope, Varia Anatolica, XX, Paris, 2009. |
|
Kassab-Tezgör 2010 |
D. Kassab-Tezgör, “Le Reseau Commercial des Amphores Sinopeennes Entre les IIe - IIIe s. et le VIe s. de Notre Ere”, Eds. D. Kassab-Tezgör – N. Inaishvili, PATABS I, Production and Trade of Amphorae in the Black Sea, Varia Anatolica, XXI (2010), 167-173. |
|
Kassab-Tezgör 2011 |
D. Kassab-Tezgör, “Types Amphoriques Romains Tardifs Produits Simultanement a Demirci pres de Sinope et dans d’autres Centres”, Eds. C. Tzochev – T. Stoyanov - A. Bozkova, PATABS II, Production and Trade of Amphorae in the Black Sea, Sofia, 2011, 259-264. |
|
Keay 1984 |
S. J. Keay, Late Roman Amphorae in the Western Mediterranean. A Typology and Economic Study: the Catalan Evidence. British Archaeological Reports International Series 196, Oxford, 1984. |
|
Kelemen 1990 |
M. H. Kelemen, “Roman amphorae in Pannonia III”, ActaArchHung. 42 (1990), 147-193. |
|
Keleş – Çelikbaş 2014 |
V. Keleş – E. Çelikbaş, “Parion Yamaç Hamamı 2008-2013”, Eds. H. Kasapoğlu – M. A. Yılmaz. Anadolu’nun Zirvesinde Türk Arkeolojisinin 40 Yılı, Ankara, 2014, 175-191. |
|
Keleş – Yılmaz 2014 |
V. Keleş – A. Yılmaz, “Parion Roma Hamamı 2006-2013”, Eds. H. Kasapoğlu – M. A. Yılmaz. Anadolu’nun Zirvesinde Türk Arkeolojisinin 40 Yılı, Ankara, 2014, 159-174. |
|
Keleş 2008 |
V. Keleş, “İlk Bulgular ışığında Parion Tiyatrosu”, Arkeoloji ve Sanat Dergisi, 128 (2008), 45-56. |
|
Keleş 2013 |
V. Keleş, “Giriş”, Ed. C. Başaran. Antik Troas’ın Parlayan Kenti, Parion, 1997-2009 Yılları Yüzey Araştırmaları, Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları, İstanbul, 2013, 19-26. |
|
Keleş et al. 2014 |
V. Keleş – A. Yılmaz – K. Oyarçin, “Parion Roma Hamamı 2013 Kazıları ve Sikke Buluntuları”, Arkeoloji ve Sanat Dergisi, 147 (2014), 21-36. |
|
Keleş et al. 2017 |
V. Keleş – H. E. Ergürer – H. Kasapoğlu – E. Çelikbaş – A. Yılmaz – B. E. Kasapoğlu – K. Oyarçin – M. D. Yılmaz – İ. Akkaş, “Parion 2015 Yılı Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları”, 38. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, Ankara, 38. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, Ankara, 2017, 23-46. |
|
Keleş et al. 2018a |
V. Keleş – E. Çeli̇kbaş – K. Oyarçin, “Bir Grup Geç Roma Sikkesi Işığında Parion Yamaç Hamamının Son Kullanım Evresi Hakkında Görüşler”, Seleucia, 8 (2018), 261-304. |
|
Keleş et al. 2018b |
V. Keleş – H. E. Ergürer – H. Kasapoğlu – E. Çelikbaş – A. Yılmaz – B. E. Kasapoğlu – K. Oyarçin – M. D. Yılmaz – İ. Akkaş, “Parion 2016 Sezonu Kazı ve Restorasyon Çalışmaları”, 39. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, I. Cilt, 2018, 183-210. |
|
Keleş et al. 2019 |
V. Keleş – H. E. Ergürer – H. Kasapoğlu – E. Çelikbaş – A. Yılmaz – B. E. Kasapoğlu – K. Oyarçin – M. D. Yılmaz – İ. Akkaş – E. Akın, “Parion 2017 Sezonu Kazı, Restorasyon ve Konservasyon Çalışmaları”, 40. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, III. Cilt, Ankara, 2019, 595-616. |
|
Kerem 1999 |
F. Kerem, İçel Müzesinden Bir Grup Amphora. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Hacettepe Üniversitesi, Ankara, 1999. |
|
Kızılarslanoğlu 2016 |
H. A. Kızılarslanoğlu, Antik Çağ’da Elaiussa Sebaste’nin Amphora Üretimi ve Ticari İlişkileri. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Atatürk Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2016. |
|
Kızılarslanoğlu 2019 |
H. A. Kızılarslanoğlu, “Elaiussa Sebaste’den Kos Origin Sorunsallı Dressel (DR) 2-4 Amphoraları”, Eds. V. Keleş – H. H. Kasapoğlu – E. Ergürer – E. Çelikbaş – A. Yılmaz, Cevat Başaran’a 60. Yaş Armağanı, Ankara, 2019, 39-70. |
|
Klenina 2000 |
E. J. Klenina, “Amphoren und Fässer“, Eds. T. Sarnowski – O. Savelja. Balaklava. Römische Militärstation und Heiligtum des Jupiter Dolicheus, Swiatowit, Suppl. Series A: Antiquity, V, Warsaw, 2000, 105-106. |
|
Konstantinidou 2010 |
A. Konstantinidou, “Aspects of Everyday Life in a Monastic Settlement: Amphorae and Cooking Wares (4th -7th c.) from the Old Monastery of Baramus in the Wadi Natrun (Egypt): A First Glance”, LRCW, 3 (1), 2010, 951-961. |
|
Konstantinidou 2012 |
A. Konstantinidou, Ceramics and Life in the Old Monastery of Baramūs in the Wādī al-Natrūn, Egypt (4th – 9th c. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Leiden Üniversitesi, Leiden, 2012. |
|
Kozal 2001 |
E. Kozal, “Studies in Roman Ilion: the Lower City. Stratified Domestic Assemblages”, Studia Troica, 11 (2001), 309-342. |
|
Körpe 2011 |
R. Körpe, “Büyük İskender’in Troas’ta İzlediği Rota ve Granikos Savaşı”, Çanakkale Araştırmaları Türk Yıllığı, 9 (10-11) (2011), 95-108. |
|
Ladstätter 1998 |
S. Ladstätter, “Afrikanische Sigillaten und Lampen aus Ovilava/Wels“, Carnuntum Jahrbuch, (1998), 51-63. |
|
Ladstätter 2008 |
S. Ladstätter, Das Vediusgymnasium in Ephesos, Ephesos XIV/1, Wien, 2008. |
|
Lako 1984 |
K. Lako, Keshtjella e onhezmit. Iliria, 2 (1984), 154-205. |
|
Lako 1993 |
K. Lako, “Te dhena per disa banesa dhe sterna te shek. II-IV te e.sone te zbuluara ne qytetin e sarandes (onhezm - Ankiazem)“, Iliria, 12 (1993), 241-257. |
|
Leidwanger 2013 |
J. Leidwanger, “Opportunistic ports and spaces of exchange in late Roman Cyprus”, Journal of Maritime Archaeology, 8 (2013), 221-243. |
|
Leidwanger 2015 |
J. Leidwanger, “Early Byzantine Cyprus: A View from the Sea”, Eds. D. N. Carlson – J. Leidwanger – S. M. Kampbell, Maritime Studies in the Wake of the Byzantine Shipwreck At Yassıada, Turkey, Texas, 2015, 157-166. |
|
Lemaitre 2007 |
S. Lemaitre, “Mobilier céramique du Létoon de Xanthos”, Ed.S. Lemaître, Céramiques antiques en Lycie (VIIe S. a. C. – VIIe S. p. C. Les produits et les marchés, Actes de la table-ronde de Poitiers, 21–22 mars 2003, Bordeaux, 2007, 115–135. |
|
Lemaitre et al. 2011 |
S. Lemaitre – G. Duperron – T. Silvino – C. Bonnet – M. Bonifay – C. Capelli. “Les amphores Africaines a Lyon du Regne d’august au VII siecle: Reflex a propos de la circulation des marchandises sur l’axe rhodanienion”, SFECAG, Actes du congres d’Arles 2011, Arles, 2011, 203-222. |
|
LRCW 1 |
Eds. J. M. Gurt Esparraguera – J.Buxeda Garrigós – M. A. Cau Ontiveros. Late Roman Coarse Wares, Cooking Wares and Amphorae in the Mediterranean, Archaeology and Archaeometry, BAR International Series 1340, Oxford, 2005. |
|
LRCW 2 |
Eds. M. Bonifay – J. C. Tréglia. Late Roman Coarse Wares, Cooking Wares and Amphorae in the Mediterranean, Archaeology and Archaeometry, BAR International Series 1662, Oxford, 2007. |
|
LRCW 3 |
Eds. S. Menchelli – S. Santoro – M. Pasquinucci – G. Guiducci. Late Roman Course Wares and Amphorae in the Mediterranean, Archaeology and Archaeometry, Comparison Between Western and Eastern Mediterranean, BAR International Series 2185, Oxford, 2011. |
|
LRCW 4 |
Eds. N. Poulou-Papadimitriou – E. Nodarou – V. Kilikoglou. Late Roman Coarse Wares, Cooking Wares and Amphorae in the Mediterranean, Archaeology and Archaeometry, The Mediterranean: a market without frontiers, BAR International Series 2616, Oxford, 2014. |
|
Lund 2007 |
J. Lund, “Transport Amphorae as a Possible Source for the Land Use and Economıc History of the Akamas Peninsula, Western Cyprus”, LRCW, 2, 2007, 781-789. |
|
Magie 1950 |
D. Magie, Roman Rule in Asia Minor. To the End of Third Century after Christ I-II, Princeton, 1950. |
|
Magness 1992 |
J. Magness, “The Late Roman and Byzantine Pottery from areas H and K. Y”, Ed. Shiloh, Excavations at the City of David 1978-1985. QEDEM, 33 (1992), 149-186. |
|
Magness 1993 |
J. Magness, Jerusalem Ceramic Chronology. Circa 200-800 CE, Sheffield, 1993. |
|
Magomedov 1991 |
B. V. Magomedov, Kamenka-Anchekrak. Poselenie Chernyakhovkoï kul’turÿ, Kiev, 1991. |
|
Magomedov 2001 |
B. V. Magomedov, Chernyakhovskaya kultura. Problema etnosa [The Chernyakhov Culture. Problems of ethnicity], Lublin, 2001. |
|
Magomedov 2010 |
B. V. Magomedov, “Roman amphorae in the context of the Chernyakov Culture”, Eds. D. Kassab-Tezgör – N. Inaishvili. Production and Trade of Amphorae in the Black Sea, Varia Anatolica XXI (2010), 75-79. |
|
Maioli – Stoppioni 1989 |
M. G. Maioli – M. Stoppioni, “Ravenna, loc. Classe. La fornace per ceramica nel Podere Chiavichetta”, Amphores Romaines et Histoire Economique (A.R.H.E.), Collection de L’Ecole Française de Rome 114 (1) (1989), 568-580. |
|
Majcherek – Zych 2011 |
G. Majcherek – I. Zych, “The evidence for Cretan presence in the ancient town of Marina el-Alamein”, Eds. W. A. Daszewski – H. Meyza – I. Zych. Essays Presented to Wiktor Andrzej Daszewski on his 75th Birthday, Classica Orientalia, Warsaw, 2011, 357-378. |
|
Majcherek 1992 |
G. Majcherek, “The Late Roman Ceramics from the Seetar "G" (Alexandria 1986-1987)”, ETTRAV, 16 (1992), 82-117. |
|
Majcherek 1993 |
G. Majcherek, “Roman Amphorae from Marina el-Alamein“, Mitteilungen des Deutschen Archaologischen Instituts Abbeilung Kairo, 49 (1993), 215-220. |
|
Majcherek 1995 |
G. Majcherek, “Gazan Amphorae: Typology Reconsidered”, Eds. H. Meyza – Y. Młynarczyk. Hellenistic and Roman Pottery in the Eastern Mediterranean- Advances in Scientific Studies, Acts of the II Nieborow Pottery Workshop 18-20 December 1993, Warsaw, 1995, 163-178. |
|
Malfitana 2008 |
D. Malfitana, “Roman Sicily Project: Ceramics and Trade. A multidisciplinary approach to the study of material culture assemblages, First overview: The transport amphorae evidence”, Facta a Journal of Roman Material Culture Studies, 2 (2008), 107-126. |
|
Manacorda 1975 |
D. Manacorda “Proposta per una dentificazione dell’anfora Dressel 24”, Archaeologia Classica, 27 (1975), 378-383. |
|
Manacorda 1977 |
D. Manacorda, “Anfore Spagnole a Pompei. Instrumentum Domesticum di Ercolano e Pompei”, Quaderni di Cultura Materiale, 1 (1977), 121-133. |
|
Manacorda 1995 |
D. Manacorda, “Sulla propietà della terra nella Calabria romana tra repubblica e impero”, Du latifundium au latifondo. Un héritage de Rome, une création médiévale ou moderne?, Actes de la table ronde internationale du CNRS organisée à l’Université Michel de Montaigne-Bordeaux III, les 17-19 décembre 1992, Paris, 1995, 143-189. |
|
Manning et al. 2000 |
S. W. Manning – S. J. Monks – D. A. Sewell – S. Demesticha, Late Roman Type 1a Amphora Production at the Late Roman site of Zygi-Petrini, Cyprus. Report of the Department of Antiquities Cyprus, 2000. |
|
Marangou-Lerat 1996 |
A. Marangou-Lerat, Le vin et les amphores de Crète : de l’époque classique à l’époque impériale, Etudes Cretoises 30, Paris, 1996. |
|
Markoulaki et al. 1989 |
S. Markoulaki – J. Y. Empereur – A. Marangou-Lerat, “Recherches sur les centres de fabrication d’amphores de Crète occidentale”, BCH 113 (1989), 551-580. |
|
Martin 2000 |
A. Martin, “Amphorae at Olympia”, RCRF, Acta, 36, 2000, 427-433. |
|
Martin-Kilcher 1994 |
S. Martin-Kilcher, Die römischen amphoren aus Augst und Kaiseraugst. Ein Beitragzur römischen Handels- und Kulturgeschichte, 3: Archaologische und Naturwissenschaftliche Tonbestimmungen, Forschungen in Augst 7/ 3, 1994. |
|
Martin-Kilcher 2005 |
S. Martin-Kilcher, ““Carthage: Imported Eastern Amphorae in the Roman Colonia Iulia”, Halicarnassian Studies III, Trade Relations in the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Hellenistic Period to Late Antiquity: The Ceramic Evidence, Odense, 2005, 202-220. |
|
Mclellan – Rautman 1994 |
M. C. Mclellan – M. L. Rautman, “The 1991-1993 field seasons at Kalavasos- Kopetra”, Report of the Department of Antiquities, Cyprus, 32 (1994), 289-307. |
|
Megaw – Jones 1983 |
A. H. S. Megaw – R. E. Jones, “Byzantine and Allied Pottery: A Contribution by Chemical Analysis to Prob1ems of Origin and Distribution”, BSA, 78 (1983), 245-247. |
|
Meyza – Baginska 2013 |
H. Meyza – D. Baginska, “Roman Amphorae from the Polish Excavations at Nea Paphos, Maloutena: An Overview”, Eds. M. L. Lawall – J. Lund, The Transport Amphorae and Trade of Cyprus, Gösta Enbom Monographs, 3, Bristol, 2013, 134-153. |
|
Mowat 2016 |
A. Mowat, The Late Roman Amphoras of Thrace: The Perspective from the Molyvoti Peninsula. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Manitoba Ünivesitesi, Winnipeg, 2016. |
|
Murialdo 2001 |
G. Murialdo, “Le anfore da transport”, S. Antonino: un insediamento fortificato nella Liguria Bizantina. Vol. 2. Bordighera: Instituto Internazionale di Studi Liguri, 2001. |
|
Negru et al. 2003 |
M. Negru – A. Bădescu – R. Avram, “Kapitän II amphorae in Roman Dacia“, RCRF, Acta, 38, 2003, 209-214. |
|
ODTÜSat 1993 |
ODTÜ Sualtı Topluluğu Batık Araştırmaları Grubu, “Antakya Kıyıları Sualtı Yüzey Araştırması 1992”, XI. Araştırma Sonuçları Toplantısı, Ankara, 1993, 60- 61. |
|
Ollà 2001 |
A. Ollà, “La produzione di anfore vinarie a Naxos (III a.C.–V d.C.)”, Ed. M. C. Lentini, Naxos di Sicilia in età romana e bizantina ed evidenze dai Peloritani. Catalogo Mostra Archeologica Museo di Naxos (3 dicembre 1999-3 gennaio 2000, Bari, 2001, 47–60. |
|
Ollà 2008 |
A. Ollà, “Anfore Romane”, Eds. R. Leone – U. Spigo, Tyndaris 1, Ricerche nel Settore Occidentale: Campagne di scavo 1993 - 2004, Sicilia, 2008, 279-287. |
|
Opait – Tsaravopoulos 2010 |
A. Opait – A. Tsaravopoulos, “A Chiote pottery workshop of the roman period”, RCRF, Acta, 41, 2010, 23-28. |
|
Opait 1991° |
A. Opait, “O sapatura de salvare in arasulantic Ibida”, SCIVA, 42 (1991), 21-56. |
|
Opait 1991b |
A. Opait,”Ceramica. Fortificatia si asezarea romana tfrzie de la Babadag-Topraichioi”, Peuce, 10 (1991b), 211-261. |
|
Opait 1996 |
A. Opait, Aspecte Ale Vietii Economice din Provincia Scythia (secolele IV-VI p.Ch.) Productia ceramicii locale şi de import, Institutul Roman de Tracologie Bibliotheca Thracologica XVI, Bucureşti, 1996. |
|
Opait 1997/98 |
A. Opait, “North african and Spanish Amphorae in Scythia Minor”, Eds. S. Alexandrescu – P. Papacostea, Il Mar Nero. Annali di archeologia e storia, III, 1997-1998, 47-95. |
|
Opait 2004° |
A. Opait, “The eastern Mediterranean amphorae in the province of Scythia”, TATEM, 2004, 293-308. |
|
Opait 2004b |
A. Opait, Local and Imported Ceramics in the Roman Province of Scythia (4th-6th centuries AD, Oxford, 2004. |
|
Opait 2009 |
A. Opait, “Cilician LR Amphora 1?”, Arheologia Moldovei, XXXII (2009), 283–289. |
|
Opait 2010 |
A. Opait, “On the Origin of Carthage LR Amphora 1”, LRCW, 3 (II), 2010, 1015-1022. |
|
Opait 2018 |
A. Opait, “Local and imported wine at Pompeiopolis, Paphlagonia”, RCRF, Acta, 45, 2018, 701-713. |
|
Opait et al. 2019 |
A. Opait – D. Davis – M. L. Brennan – M. Kofahl, “The Sinop F Shipwreck in the Black Sea: An International Cargo from Late Antiquity”, Eds. H. Kaba – G. Kan Şahin – B. M. Akarsu – O. Bozoğlan, International Symposium on Sinope and Black Sea Archaeology “Ancient Sinope and the Black Sea”, Sinop, 2019, 77-89. |
|
Orhan 2017 |
U. Orhan, “Phaselis 2016 Yılı Güney Limanı Amphora Buluntuları”, Phaselis, III (2017), 141-148. |
|
Orhan 2018 |
U. Orhan, Kekova Sualtı Araştırmalarında Tespit Edilen Amphoralar. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Selçuk Üniversitesi, Konya, 2018. |
|
Outschar 1993 |
U. Outschar, Produkte aus Ephesos in alle welt? ÖAI 5, Wien, 1993. |
|
Oyarçin 2017 |
K. Oyarçin, Parion’da 2005-2015 Yılları Arasında Ele Geçen Geç Roma ve Erken Bizans Dönemi Sikkeleri (MS 3-7. Yüzyıl). Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Erzurum Üniversitesi, Erzurum, 2017. |
|
Özkan 2020 |
Özkan, H. Parion Kemik Eserler 2005-2017. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Ondokuz Mayıs Üniversitesi, Samsun, 2020. |
|
Özsait 1999 |
M. Özsait, “Küçük Asya’da Roma Kolonileri“. Ed. N. Başgelen, Zafer Taşlıklıoğlu Armağanı Anadolu ve Trakya Çalışmaları I, İstanbul, 1999, 123-132. |
|
Pacetti 1998 |
F. Pacetti, “La questione delle Keay LII nell’ambito della produzione anforica in Italia”, Ed. L. Sagui, Ceramica in Italia: VI-VII sec., Atti del Convegno in onore di John W. Hayes, Roma, 11-13 maggio 1995. Biblioteca di Archeologia Medievale, Firenze, 1998, 185–208. |
|
Pallarès 1987 |
F. Pallarès, “Alcune considerazione sulle anfore del Battistero di Albenga”, RELig, LIII (1-4) (1987), 269-306. |
|
Panella 1970 |
C. Panella, “Anfore”, Ostia II, Le terme del Nuotatore: Scavo dell’ambiente I (1970), 102-156. |
|
Panella 1973 |
C. Panella, “Appunti su un Gruppo di Anfore della Prima, Media e Tarda Età Imperiale“. Ostia III: Le terme del Nuotatore: Scavo dell’ambiente V et di un saggio dell’area, Studi miscellenei, 21 (1973), 463-633. |
|
Panella 1976 |
C. Panella, “Per uno studio delle anfore di Pompei. Le forme VIII e X della tipologia di R. Schoene“, Studi miscellenei, 22 (1976), 151-162. |
|
Panella 1982 |
C. Panella, “Le anfore della prima, media e tarda età imperiale: tipologia e problem”, Actes du colloque sur la céramique antique (Carthage, 23-24 juin 1980), Carthage, 1982, 171-196. |
|
Panella 2001 |
C. Panella, “Le anfore di eta imperiale del Mediterraneo occidentale”, Céramiques Hellénistiques et Romaines, III (2001), 177-275. |
|
Panella et al. 2010 |
C. Panella – L. Sagui – M. Casalini – F. Coletti, “Contesti tardoantichidi Roma: Una rilettura alla luce di nuovi dati”, LRCW, 3 (1), 2010, 57-78. |
|
Papadopoulos 1989 |
J. K. Papadopoulos, “Roman Amphorae from The Torone”, Aephem, (1989), 67-103. |
|
Parlak 2019 |
K. Parlak, Parion Kazılarında Ele Geçen Bizans Dönemi Sikkeleri 2015-2018. Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Ondokuz Mayıs Üniversitesi, Samsun, 2019. |
|
Pausanias |
Pausanias, Pausanias’da Anadolu, Seçmeler, (Çev. B. Umar), İstanbul, 2002. |
|
Peacock – Williams 1986 |
D. P. S. Peacock – D. F. Williams, Amphorae and the Roman Economy, London, 1986. |
|
Peacock 1984 |
D. P. S. Peacock, “The Amphorae: Typology and Chronology”, Eds. M. G. Fulford – D. P. S. Peacock, Excavations at Carthage: The British Mission, Vol. I, 2, The avenue du Président Habib Bourguiba, Salambo: The Pottery and other Ceramic Objects from the site, Sheffield, 1984, 116-140. |
|
Peacock et al. 1989 |
D. P. S. Peacock – F. Béjaoui – N. Ben-Lazreg, “Roman Amphora Production in the Sahel Region of Tunisia”, Amphores romaines et histoire économique, dix ans de recherche. Actes du colloque de Sienne (22-24 Mai 1986), Rome, 1989, 179-222. |
|
Peacock et al. 1990 |
D. P. S. Peacock – F. Bejaoui – N. Ben-Lazreg, “Roman pottery production in central Tunisia”, Journal of Roman Archaeology, 3 (1990), 59-84. |
|
Pichot – Şenol 2015 |
V. Pichot – K. Şenol, “Amphores de Gaza et résine sur le site de production d’amphores du Haut- Empire d’Akadémia (Maréotide)”, Bulletin de Liaison du Groupe International D’étude de la Céramique Égyptienne, 25 (2015), 277-289. |
|
Pieri 2005 |
D. Pieri, Le commerce du vin oriental à l’époque Byzantine, Beirut, 2005. |
|
Pieri 2007 |
D. Pieri, “ Béryte dans le grand commerce méditerranéen : Production et importation d’amphores dans le Levant protobyzantin (Ve-VIIe s. apr. J.-C.)”, Ed. M. Sartre, Productions et échanges dans la Syrie Gréco-Romaine, Actes du 2e Colloque International sur la Syrie Antique (Tours, 12-13 juin 2003), suppl. Topoï, 8, 2007, 297-327. |
|
Portale – Romeo 2001 |
E. Portale – I. Romeo, “Contenitori da trasporto”, Ed. A. D. Vita, Gortina V.3. Lo scavo del Pretorio 1989-1995), 1. I materiali, Padova, 2001, 260-410. |
|
Portale 2010 |
E. Portale, “Nuovi Dati Sulla Circolazione Anforica a Gortina”, LRCW, 3 (1), 2010, 931-939. |
|
Poulou-Papadimitriou – Nodarou 2007 |
N. Poulou-Papadimitriou – E. Nodarou, “La céramique protobyzantine de Pseira: la production locale et les importations, étude typologique et pétrographique”, LRCW, 2 (II), 2007, 755-766. |
|
Preda – Grosu 1993 |
C. Preda – A. Grosu, “Cercetări arheologice din aşezarea civilă a castrului roman de la Enoşeşti - Acidava (Piatra Olt, jud. Olt)”, Arhivele Olteniei, 8 (1993), 43-55. |
|
Prêteux 2009 |
F. Prêteux, “Parion et son territoire à l’époque hellénistique: un exemple d’organisation de la chôra sur le rivage de la Propontide”, Eds. H. Bru – F. Kirbihler – S. Lebreton. L’Asie mineure dans l’Antiquité: échanges, populations et territoires: Regards actuels sur une péninsule, Rennes, 2009, 335-350. |
|
Pülz 1985 |
S. Pülz, “Studien zu einzelnen fundgriuppen-Kaiserizeitliche Keriamik aus dem Herioon III“,IstMitt 35 (1985), 77-115. |
|
Radaelli 2016 |
E. Radaelli, Amphorae from contexts of middle Imperial date found during the excavations of the so-called ‘Terme di Elagabalo’ in Rome. The implications of their study for our understanding of the economy of the City and of related imported products. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Southampton Üniversitesi, Southampton, 2016. |
|
Ramon 1986 |
J. Ramon, El Baix Imperi i l’época Bisantina a les Illes Pitiuses, Ibiza, 1986. |
|
Rauh 2004 |
K. Rauh – N. “Pirated Knock-offs: Cilician Imitations of Internationally Traded Amphoras”, TATEM, 2004, 329-336. |
|
Rautman 1995 |
M. L. Rautman, “Two Late Roman wells at Sardis”, AASOR 53 (1995), 37-84. |
|
Rautman 2000 |
M. L. Rautman, “The Busy Countryside of Late Roman Cyprus”, Report of the Department of Antiquities Cyprus, 38 (2000), 317-331. |
|
Rautman 2003 |
M. L. Rautman, A Cypriot Village of Late Antiquity: Kalavasos-Kopetra in the Vasilikos Valley, JRA Supplement 52, Portsmouth, 2003. |
|
Rautman et al. 1993 |
M. L. Rautman – B. Gomez – H. Neff – M. D. Glascock, “Neutron Activation of Late Roman Ceraınics from Kalavassos-Kopreta and the Environs of the Vasilikos Valley”, Report of The Department of Antiquities Cyprus, 31 (1993), 233-294. |
|
RCRF |
Rei Cretariae Romanae Favtorvm |
|
Remola-Vallverdu 1989 |
J. A. Remola-Vallverdu, “ Les àmfores”, Un abocador del segle V d.. C. en el fòrum provincial de Tàrraco, Tarragone, 1989, 249-323. |
|
Remola-Vallverdu 1993 |
J. A. Remola-Vallverdu, “Un tipo de anfora tardo-romana poco conocido (VLR 8. 198)”, Archivo Español de Arqueología, 66 (1993), 301-309. |
|
Remola-Vallverdu 2000 |
J. A. Remola-Vallverdu, Las ànforas tardo-antiguas en Tarraco (Hispania Tarraconensis), Barcelona, 2000. |
|
Remola-Vallverdu 2007 |
J. A. Remola-Vallverdu, “Tarraco, amphores et contexte Historique”, Eds. A. Mrabet – J. Remesal Rodriguez, Africa et in Hispania: études sur L’huile Africaine, Collecio instrumenta 25, Barcelona, 2007, 245-256. |
|
Reynolds – Pavlidis 2014 |
P. Reynolds – E. Pavlidis, “Nicopolis (Epirus Vetus): An Early 7th Century Pottery Assemblage from the ‘Bishop’s House’ (Greece)”, LRCW, 4 (I), 2014, 451-467. |
|
Reynolds 2004 |
P. Reynolds, “The Roman pottery from the Triconch Palace”, Eds. R. Hodges – W. Bowden – K. Lako – R. D. Andrews, Byzantine Butrint: Excavations and surveys 1994-1999, Oxford, 2004, 224-269. |
|
Reynolds 2005 |
P. Reynolds, “Levantine amphorae from Cilicia to Gaza: a Typology and Analysis of Regional Production Trends from the 1st to 7th Centuries”, LRCW, 1, 2005, 563-612. |
|
Reynolds 2010 |
P. Reynolds, “Trade networks of the East, 3rd to 7th Centuries: the view from Beirut (Lebanon) and Butrint (Albania) (Fine Wares, Amphorae and Kitchenwares”, LRCW, 3 (1), 2010, 89-114. |
|
Reynolds 2011 |
P. Reynolds, “A 7th century pottery deposit from Byzantine, Carthago Spartaria Cartagena, Spain”, Eds. M. À. Cau – P. Reynolds – M. Bonifay, LRFW 1, Late Roman Fine Wares: Solving problems of typology and chronology. A review of the evidence, debate and new contexts (RLAMP 1), Oxford, 2011, 99-127. |
|
Reynolds 2013 |
P. Reynolds, “Transport Amphorae of the First to Seventh Centuries: Early Roman to Byzantine Periods”, Ed. W. Aylward. Excavations at Zeugma, Conducted by Oxford Archaeology, Volume II, Oxford, 2013, 93-161. |
|
Reynolds 2019 |
P. Reynolds, Butrint 6 Excavations on the Vrina Plain Volume 3: The Roman and Late Antique Pottery from the Vrina Plain Excavations, Oxford, 2019. |
|
Ricci 2007 |
M. Ricci, “Elaiussa Sebaste: Context, Production & Commerce”, BYZAS 7, Istanbul, 2007, 169-180. |
|
Riley 1975 |
J. A. Riley, “The Pottery from the First Session of Excavation in the Caesarea Hippodrome”, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, 218 (1975), 25-63. |
|
Riley 1979 |
J. A. Riley, “The coarse pottery from Berenice”, Ed. J. A. Lloyd, Excavations at Sidi Khrebish Benghazi (Berenice): Volume II. Tripoli: Dept. of Antiquities, Secretariat of Education, London, 1979, 91-467. |
|
Riley 1981 |
J. A. Riley, “The pottery from the cisterns 1977.1, 1977.2, 1977.3”, Ed. J. H. Humphrey, Excavations at Carthage 1975-1979: Conducted by the University of Michigan. Vol. 6, Tunus, 1981, 85-124. |
|
Rizzo – Zambito 2010 |
G. Rizzo – G. Zambito, “Ceramiche Comuni ed Anfore dal Villaggio Tardoantico di Cignana, Naro-Agrigento, Sicilia, Italia”, LRCW, 3 (I), 2010, 293-300. |
|
Rizzo 2003 |
G. Rizzo, Instrumentua Vrbis. 1, Ceramiche fine da mensa, lucerne ed anfore a Roma nei primi due secole dell’impero, Rome, 2003. |
|
Rizzo 2014 |
G. Rizzo, “Le Terme del Nuotatore le Anfore, Ostia e i Commerci Mediterranei”, Eds. C. Panella – G. Rizzo, OSTIA VI, Le Terme del Nuotatore, Studi Miscellanei 38, Roma, 2014, 64-442. |
|
Robinson 1959 |
H. S. Robinson, Pottery of the Roman Period. Chronology. (The Athenian Agora. Results of excavations conducted by the American School of Classical Studies, vol. v.), Princeton, 1959. |
|
Romanchouk et al. 1995 |
A. Romanchouk – A. V. Sazanov – L. Sedikova, Les amphares des ensembles de Chersonese Byzantin, Ekaterinbourg, 1995. |
|
Rowe 2004 |
A. H. Rowe, Nea paphos: Reconsidering Late Roman Cyprus: Using New Material from Nea Paphos to Review Current Artefact Typologies. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Sydney Üniversitesi, Sydney, 2004. |
|
Sagui 1998 |
L. Sagui, “Il deposito della Crypta Balbi: una testimonianza imprevedibile sulla Roma del VII secolo? Ed. L. Sagui, Ceramica in Italia: VI-VII secolo”, Atti del Convegno in onore di John W. Hayes (Roma, 11-13 maggio 1995), Firenze, 1998, 305-333. |
|
Santamaria 1995 |
C. Santamaria, L’épave Dramont « E » à Saint-Raphaël (Ve siècle ap. J.-C.) Archaeonautica, 13, Paris, 1995. |
|
Sayar 2015 |
M. H. Sayar, “Parion’da Divus Vespasianus Augustus’a Bir Sunu”, Eds. C. Başaran – V. Keleş, Parion Kazıları 10. Yıl Armağanı, Ankara, 2015, 163-166. |
|
Sazanov 1989 |
A. Sazanov, “O khronologii Bospora rannevizantiiskogo vremeni”, Sovetskaia Arkheologiia, 4 (1989), 41-60. |
|
Sazanov 1991 |
A. Sazanov, “Les amphores de l’ensemble du preinier quart du vne s. de la region nord-est de Chersonese”, MANIET, 2 (1991), 60-72. |
|
Sazanov 1997 |
A. Sazanov, “Les Amphores de L’Antiquité Tardive et du Moyen Age: Continuité ou Rupture? Le Cas de la mer Noire”, La Céramique Médiévale en Mediterranée, Actes Du VIE Congrès de L’aiecm 2, (13-18 novembre 1995), Aix-en-Provence, 1997, 87-102. |
|
Sazanov 1999 |
A. Sazanov, “Les Amphores “LA 1 Carthage” dans la Region de la mer Noire”, Ed. C. Y. Garlan, Typologie et Chronologie: Ve -VIIe s. Apr. J, Aix-en-Provence, 1999, 265-279. |
|
Sazanov 2000 |
A. Sazanov, “Les ensembles clos de Chersonese de la fin du VIe-troisieme quart du VIIe siecles: la chronologie de la ceramique”, Les sites archeologiques en Crimee et au Caucase durant l’antiquite tardive et le haut moyen-age, Colloquia Pontica, Leiden, 2000, 123-149. |
|
Sazanov 2014 |
A. Sazanov, “The Deposit of the end of the 6th Century AD from Chersonesos, Crimea”, LRCW, 4 (I), 2014, 411-423. |
|
Scorpan 1976 |
C. Scorpan, “Origini si linii evolutive in ceramica romano- bizantina (sec. IV—VII) din”, Spatiul Mediteranean si Pontic, 9 (1976), 155-185. |
|
Scorpan 1977 |
C. Scorpan, “Contribution a la Connaissance de Certains Types Ceramiques Romano- Byzantins (IVe – VIIe Siecles) dans L’Espace Istro-Pontique”, Dacia, XXI (1977), 269-296. |
|
Seyer 2014 |
M. Seyer, “Limyra 2013”, ANMED, 12, 73-80. |
|
Shkodra 2003 |
B. Shkodra, Pottery and trade in the Late Roman Durres (Durrachium). Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, East Anglia Üniversitesi, Bükreş, 2003. |
|
Shkodra 2005 |
B. Shkodra, “Kontekste me qeramikë të shek. VI nga Macellum“, Candavia, 2 (2003), 205-238. |
|
Shkodra 2006 |
B. Shkodra, “Ceramics from Late Roman Contexts in Durrës”, BSA 101 (2006), 427-457. |
|
Shkodra 2009 |
B. Shkodra, “Një tip amfore i periudhës antike të vonë nga Durrësi”, Iliria, XXXIII (2009), 311-324. |
|
Silvino 2007 |
T. Silvino, “Lyon. La fouille du pare Saint-Georges: le mobilierceramique de I’antiquite tardive”, Revue Archeologique de I’Est, 56 (2007), 187-230. |
|
Slane - Sanders 2005 |
K. W. Slane – G. R. Sanders, “Corinth: Late Roman Horizons”, Hesperia 74 (2) (2005), 243-297. |
|
Slane 2000 |
K. W. Slane, “East-West Trade in Fine Wares and Commodities: the View from Corinth”, RCRF, Acta, 36, 2000, 299-311. |
|
Smokotina 2016 |
A. Smokotina, “Late Roman Amphorae from Tyritake”, RCRF, Acta, 44, 2016, 715–724. |
|
Stănescu 2018 |
R. O. Stănescu, “Amphorae Ex Aegysso: Fragments from Older Excavations”, Peuce, XVI (2018), 205-226. |
|
Starac 2001 |
A. Starac, “Produzione e distribuzione delle anfore nord-adriatiche nell’Istria”, RCRF, Acta, 37 (2001), 269–277. |
|
Suceveanu 2000 |
A. Suceveanu, Histria X. La céramique romaine des Ier–IIIe siècles ap. J.-C. Bucarest, 2000. |
|
Suceveanu 2007 |
A. Suceveanu, Histria XIII. La Basilique Épiscopale, Paris, 2007. |
|
Swan 2004 |
V. G. Swan, “Dichin (Bulgaria) and the supply of amphorae to the Lower Danube in the late Roman-early Byzantine period”, TATEM, 2004, 371-382. |
|
Şen 2017 |
D. Şen, La Ceramique ProtoByzantine De Lycie: etude du mobilier Hurmalık Hammam de Patara. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Paris 1- Pantheon Sorbonne Üniversitesi, Paris, 2017. |
|
Şenol – Aşkın 2007 |
A. K. Şenol – E, Aşkın. “Amphoralar Işığında Kentin Ticarî İlişkileri“, Ed. S. Durugönül, Dağlık Kilikia’da Bir Antik Kent Kazısının Sonuçları NAGIDOS, Adayla Ekyayın Dizisi 6, Antalya, 2007, 241-297. |
|
Şenol 2000 |
A. K. Şenol, İskenderiye Kazılarında Ele Geçen Amphoralar Işığında Kentin Roma Dönemi Şarap, Zeytinyağı, Salamura Balık ve Sos Ticareti. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Ege Üniversitesi, İzmir, 2000. |
|
Şenol 2001 |
A. K. Şenol, “Amphoras from the Necropolis of Gabbari”, Eds. J. Y. Empereur – M. D. Nenna, Nécropolis 1, Etudes Alexandrines 5, Caire, 2001, 369-396. |
|
Şenol 2003a |
A. K. Şenol, Marmaris Müzesi Ticarî Amphoraları, Ankara, 2003. |
|
Şenol 2003b |
A. K. Şenol, “The Amphoras Handles from the Bridge Excavations, Gabbari Sector 2”, Eds. J. Y. Empereur – M. D. Nenna, Nécropolis 2, Etudes Alexandrines 7, Caire, 2003, 191-211. |
|
Şenol 2007 |
A. K. Şenol, “A Statistical Essay on the Distribution of Imported Amphorae Finds of the CEAlex Salvage Excavations”, Eds. S. Marchand – A. Marangou, Amphores D’Egypte, de la Basse Epoque a l’Epoque Arabe, I, Alexandreia, 2007, 57- 75. |
|
Şenol 2009 |
A. K. Şenol, AETAM (Arslan Eyce Taşucu Amphora Müzesi)’da Bulunan Ticarî Amphoralar ve Akdeniz’de Ticaretin İzleri, Mersin, 2009. |
|
Şenol 2015 |
A. K. Şenol, “Smyrna Kazılarında 2007 2011 Yılları Arasında Bulunan Ticari Amphoralar”, Ed. A. Ersoy, 1. Smyrna Antik Kenti Kazı ve Araştırmaları Çalıştayı, 2-3 Mayıs 2014, İzmir, İstanbul, 2015, 243-256. |
|
Şenol 2018 |
A. K. Şenol, Commercial amphorae in the Graeco-Roman Museum of Alexandria, Alexandreia, 2018. |
|
Şen-Yıldırım 2012 |
D. Şen-Yıldırım, “Hurmalık Hamamı Buluntuları Işığında Patara’nın Geç Roma-Erken Bizans Dönemi Kuzey Afrika Kökenli Seramikleri”, Anadolu Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 12 (4) (2012), 151-172. |
|
TATEM |
Eds. J. Eiring - J. Lund. Transport Amphorae and Trade in the Eastern Mediterranean, Monographs of the Danish Institute at Athens Volume 5, Athens, 2004. |
|
Tekocak – Zoroğlu 2013 |
M. Tekocak – L. Zoroğlu, “Kelenderis’te Bulunan Bir Grup Roma Dönemi Ticari Amphorası ve Düşündürdükleri”, Olba, XXI (2013), 109-140. |
|
Tomber 1993 |
R. Tomber, “Quantitative Approaches to the Investigation of Long-Distance Exchange”, JRA, 6 (1993), 142-166. |
|
Tomber 1999 |
R. Tomber, “Pottery from the sediments of the Inner Harbour (Area 114)”, Caesarea Papers, 2 (1999), 296-321. |
|
Tomber 2006 |
R. Tomber, “The Pottery”, Eds. V. A. Maxfield – D. P. S. Peacock, Survey and Excavation Mons Claudianus, 1987-1993, Volume III, Ceramic Vessels & Related Objects, Fouilles de L’Ifao 54, Paris, 2006, 3-218. |
|
Tomber 2008 |
R. Tomber, Indo–Roman Trade. From pots to pepper, London, 2008. |
|
Tüylüoğlu 2015 |
D. Tüylüoğlu, Mylasa’dan Bir Antik Çağ Seramik Atölyesinin (?) Ticari Amphora Buluntuları, Yayımlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman Üniversitesi, Muğla, 2015. |
|
Uzhentsev – Yurochkin 1998 |
V. B. Uzhentsev – V. Yurochkin, “Amphores a col en entonnoir au nord de la mer Noire”, Khersoneskii Sbornix, IX (1998), 100-109. |
|
Uzhentsev 2001 |
V. B. Uzhentsev, “Kalos Limen in the 1st c. B.C. - beginning of the 1st c. AD (general review of the materials according to the excavations in 1988-1998)”, Eds. I. I. Gushchina – D. V. Zhuravle, Pozdnie Skify Kryma [Late Scythians in Crimea], Moscow, 2001, 156-166. |
|
Villedieu 1984 |
F. Villedieu, Turris Libisonis. Fouille d’un site romain tardif à Porto Torres (Sardaigne), BAR International Series 224, Oxford, 1984, 166-199. |
|
Villedieu 1990 |
F. Villedieu, Lyon St-Jean, les fouilles de l’avenue Adolphe Max, Documents d’Archéologie en Rhône-Alpes (DARA) 3, Lyon, 1990. |
|
Vilvorder et al. 2000 |
F. Vilvorder – R. P. Symonds – S. Rekk, “Les amphores orientales en Gaule septentrionale et au sud–est de la Grande Bretagne“. RCRF, Acta, 36, 2000, 477–486. |
|
Vnukov 2004 |
S. Vnukov, “Pan-Roman Amphora Types Produced in the Black Sea Region”, TATEM, 2004, 407-415. |
|
Vnukov 2010 |
S. Vnukov, “Sinopean Amphorae of the Roman Period”, Ancient Civilizations from Scythia to Siberia, 16 (2010), 361-370. |
|
Vnukov 2012 |
S. Vnukov, “Амфорное Производство На Территории Абхазии В Эпоху Эллинизма И Римское Время (Amphora Production on the Territory of Abkhazia during the Hellenistic Era and Roman Time)”, Российская Археология (Russian Archeology), 4 (2012), 5-15. |
|
Vogt 1997 |
C. Vogt, “Les ceramiques ommeyyades et abbassides d’Istabl’ Aııtar-Fostat”, Ed. G. D. Archimbau, La céramique médiévale en Méditerranée: Actes du VIe congès de l’AIECM2, Aix-en-Provence, 1997, 243-260. |
|
Vogt et al. 2002 |
C. Vogt – P. Gouin – G. Bourgeois – M. Girard – M. Schvoerer – S. Thiebault, “Notes on Some of the ‘Abbasid Amphorae of Istabl ‘Antar- Fustat (Egypt)”, BASOR 326 (2002), 65-80. |
|
Volpe 1985 |
G. Volpe, “Anfore”, Ed. S. Caterina d ella Rosa, Il giardino del Conservatorio. Arclıeologia w·bana a Roma: il rogetto della Crypta Balbi, 3, 1985, 155-172. |
|
Warner-Slane 2000 |
K. Warner-Slane, “East–West Trade in Fine Wares and Commodities. The View from Corinth”, RCRF, Acta, 36, 2000, 299–312. |
|
Watson 1992 |
P. M. Watson, “Change in Foreign and Regional Economic Links with Pella in the Seventh Century AD: The Ceramic Evidence”, La Syrie de Byzance a l’Islam, VIf-VIIf siecles, actes du colloque international (Lyon-Paris, 11-15 septembre 1990), Damas, 1992, 233-248. |
|
Watson 1995 |
P. M. Watson, “Ceramic Evidence for Egyptian Links with Northern Jordan in the 6th -8th Centuries AD”, Eds. S. Bourhe – J. P. Descoeudres, Trade, Contact and the Movement of Peoples in the Eastern Mediterranean, Mediterranean Archaeology, suppl. 3, Sydney, 1995, 314-319. |
|
Whitbread 1995 |
I. K. Whitbread, Greek Transport Amphorae. A Petrological and Archaeological Study, Athens, 1995. |
|
Williams 1979 |
D. F. Williams, “The Heavy Mineral Separation of Ancient Ceramics by Centrifugation: A Preliminaıy Report”, Archaeometry, 21 (1979), 177-182. |
|
Williams 1980 |
D. F. Williams, “The Petrology of Certain Byzantine Amphorae: Some Suggestions as to Origins”, Ancient Monuments Laboratoy Report, 3115 (1980), 99-110. |
|
Williams 1989 |
C. Williams, “Anemurium, The Roman and Early Byzantine Pottery”, Subsidia Mediaevalia 16 (1989), 90-99. |
|
Williams 1990 |
D. F. Williams, “A note on the petrology of a Samos cistern type amphora from excavations at the Castello di Udine”, Aquileia Nostra Anno, LXI (1990), 281-296. |
|
Williams 2004 |
D. F. Williams, “The Eruption of Vesuvius and Its Implications for the Early Roman Amphora Trade with India”, TATEM, 2004, 441–450. |
|
Williams 2005 |
D. F. Williams, “Late Roman Amphora 1: A Study of Diversification”, Eds. M. B. Briese – L. E. Vaag, Halicarnassian Studies III, Trade Relations in the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Hellenistic Period to Late Antiquity: The Ceramic Evidence, Odense, 2005, 157-167. |
|
Williams et al. 1974 |
C. K. Williams – J. Mclntosh – J. E. Fisher, “Excavations at Corinth, 1973”, Hesperia, 43 (1) (1974), 1-76. |
|
Yaman 2018 |
A. Yaman, Arykanda Geç Antik Dönem Mahallesi Seramikleri. Yayımlanmamış Doktora Tezi, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman Üniversitesi, Muğla, 2018. |
|
Yangaki 2005 |
A. G. Yangaki, La céramique des IVe-VIIIe siècles ap. J.-C. D’Eleutherna: sa place en Créte et dans le bassin égéen, Athènes, 2005. |
|
Yangaki 2007 |
A. G. Yangaki, “Amphores crétoises de forme globulaire: remarques préliminaires”, LRCW, 2 (II), 2007, 767 - 774. |
|
Yener-Marksteiner 2013 |
B. Yener-Marksteiner, “Vorlaufige Ergebnisse der Untersuchungen der Keramikfunde des Andriake-Surveys“. Eds. P. Brun – L. Cavalier – K. Konuk – F. Prost, EUPLOIA. La Lycie et la Carie antiques. Dynamiques des territoires, échanges et identités. Actes du colloque de Bordeaux 5, 6, 7 novembre 2009, Paris, 2013, 15-20. |
|
Zachariadis 2014 |
S. Zachariadis, “Pottery from the Workshop Building, in the Early Byzantine City of Philippi, Greece”, LRCW, 4 (I), 2014, 705-713. |
|
Zeest 1960 |
I. B. Zeest, Keramicheskaia Tara Bospora, Moskova, 1960. |
|
Zemer 1977 |
A. Zemer, Storage Jars in Ancient Sea Trade, Haifa, 1977. |
İ. Akkaş, “Parion Yamaç Hamamı Ticari Amphora Buluntuları (MÖ 1. yüzyıl - MS 7. yüzyıl)”, Arkhaia Anatolika 3 (2020), 178-243. DOI: 10.32949/Arkhaia.2020.21